FIG 7.
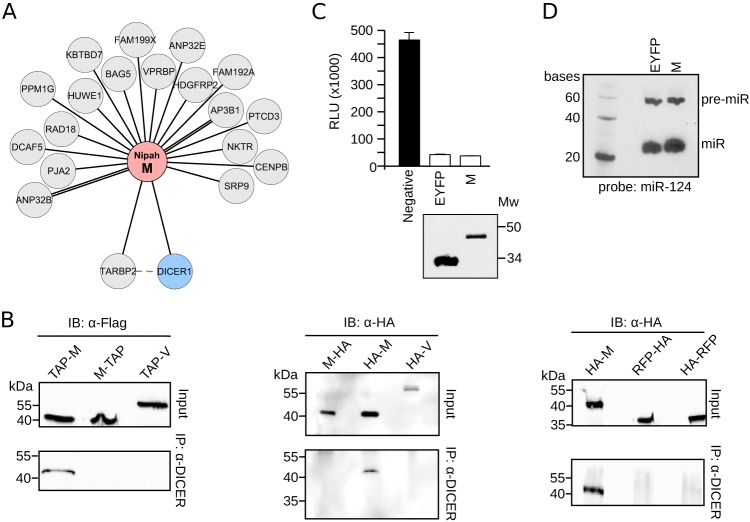
Interaction of Nipah virus M with the DICER1-TARBP2 complex. (A) Network representation of the Nipah virus M protein interaction with cellular proteins. (B, left) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous DICER1 in HEK293T cells transfected with Nipah virus M and V proteins (M-TAP and TAP-M and V-TAP) (TAP tagged either at the amino terminus, TAP-M, or the carboxyl end, M-TAP and V-TAP). (Middle and right) Immunoprecipitation of endogenous DICER1 in HEK293T cells transfected with Nipah virus M and V proteins and RFP tagged with an HA flag at the indicated terminus. IB, immunoblot. (C) DICER1 activity assay. HEK293T cells were transfected with luciferase plasmids containing mir124 target sites plus a plasmid expressing mir124. In the absence of mature miR124, expression of Luc is unhampered. Conversely, DICER1-dependent production of mature miR124 blocks Luc expression. The black bar indicates a negative control comprised of cells expressing Luc but no miR124 plasmid. White bars include EYFP (positive) and W samples. A Western blot was included to confirm the expression of EYFP and the Nipah virus M protein. Mw, molecular weight (in thousands). (D) Northern blot of pre-miR124 (pre-miR) and mature miR124 in cells expressing EYFP or the Nipah virus M protein.