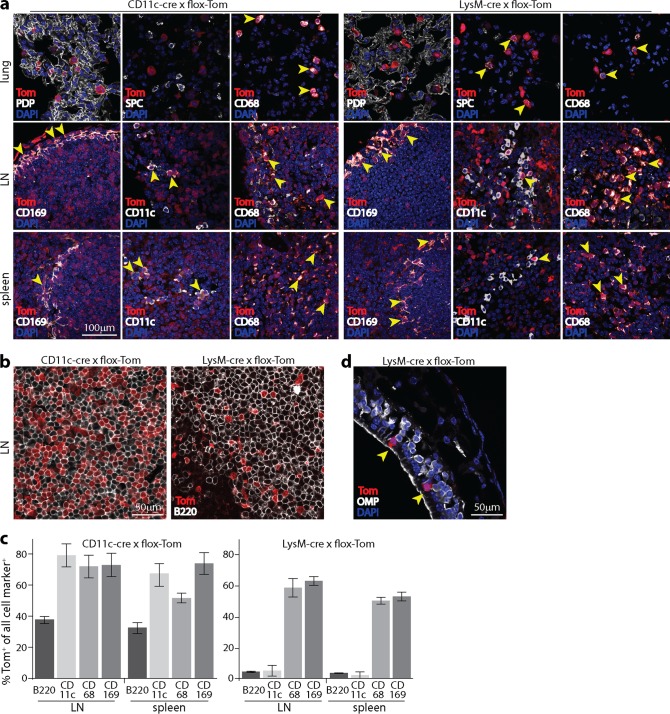
FIG 4.
Distribution of lymphoid cre expression in CD11c-cre and lysM-cre mice. (a) Naive CD11c-cre × flox-Tom and lysM-cre × flox-Tom mice were analyzed for tdTomato (Tom) expression in tissue sections. In lungs, CD11c-cre expression gave Tom+ AM (CD68+) but not AEC1 (PDP+) or AEC2 (SPC+). lysM-cre expression gave Tom+ AEC2 and AM. In LN, the expression of both CD11c-cre and lysM-cre gave Tom+ SSM (CD169+) and other Tom+ myeloid cells (CD68+). CD11c-cre labeled most DC (CD11chi). LysM-cre labeled <10% of DC. In spleens, both CD11c-cre and lysM-cre labeled myeloid cells in the MZ. CD11c-cre labeled most (although not all) CD11c+ cells, while lysM-cre labeled <5% of CD11c+ cells. (b) Example Tom+ fluorescence in B220+ cells of CD11c-cre+ and lysM-cre+ LN. (c) Summary of Tom expression in LN and spleens of lysM-cre+ and CD11c-cre+ mice. Bars show the mean percentages of Tom+ cells ± standard errors of the means for each cell type marker. Cells counts are for at least 3 sections per organ. (d) The olfactory epithelium of lysM-cre × flox-Tom mice contains occasional Tom+ cells, but they are OMP− and thus are not olfactory neurons. They also lack the characteristic epithelium-spanning morphology of sustentacular cells and thus seem likely to be intraepithelial myeloid cells.