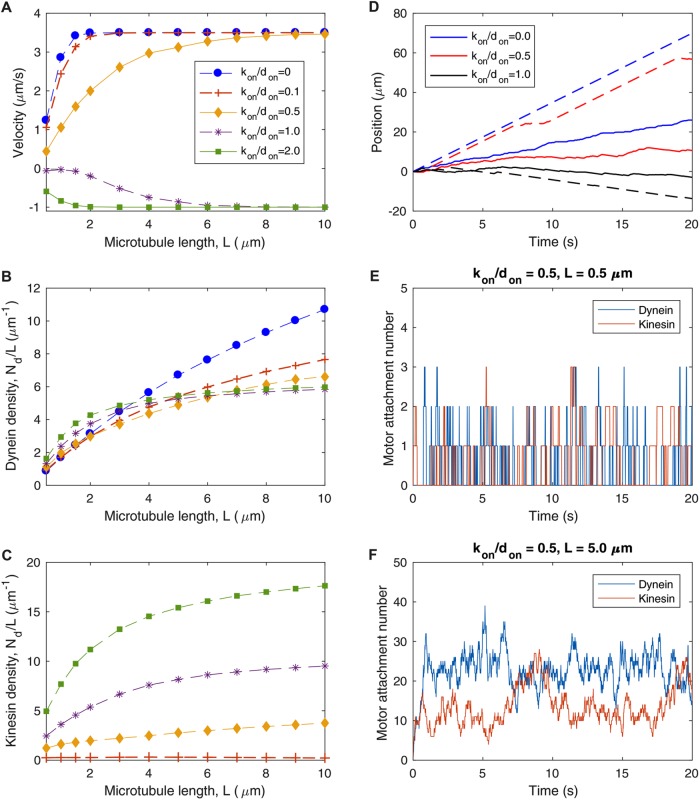
FIGURE 4:
Competition between cytoplasmic dynein and kinesin-1 does not explain immobility of long axonal MTs. Parameters in Table 1, don = 0.1 s−1, and xon = 0 are used for all simulations. (A) Time-averaged velocity of MT transport as a function of MT length for various values of the ratio of kinesin attachment rate to dynein attachment rate, kon/don. (B) Average dynein attachment density, Nd/L, as a function of MT length L, for the same values of kon/don as in A. (C) Average kinesin attachment density, Nk/L, as a function of MT length L, for the same values of kon/don as in A. (D) Sample trajectories for several values of kon/don, with solid lines corresponding to short MTs of length L = 0.5 μm and dashed lines corresponding to longer MTs of length L = 5.0 μm. Solid lines and dashed lines of the same color correspond to the same kon/don, as specified in the legend. (E) Dynein and kinesin motor attachment numbers as a function of time for kon/don = 0.5 and L = 0.5 μm, corresponding to the solid red line in D. (F) Dynein and kinesin motor attachment numbers as a function of time for kon/don = 0.5 and L = 5.0 μm, corresponding to the dashed red line in D.