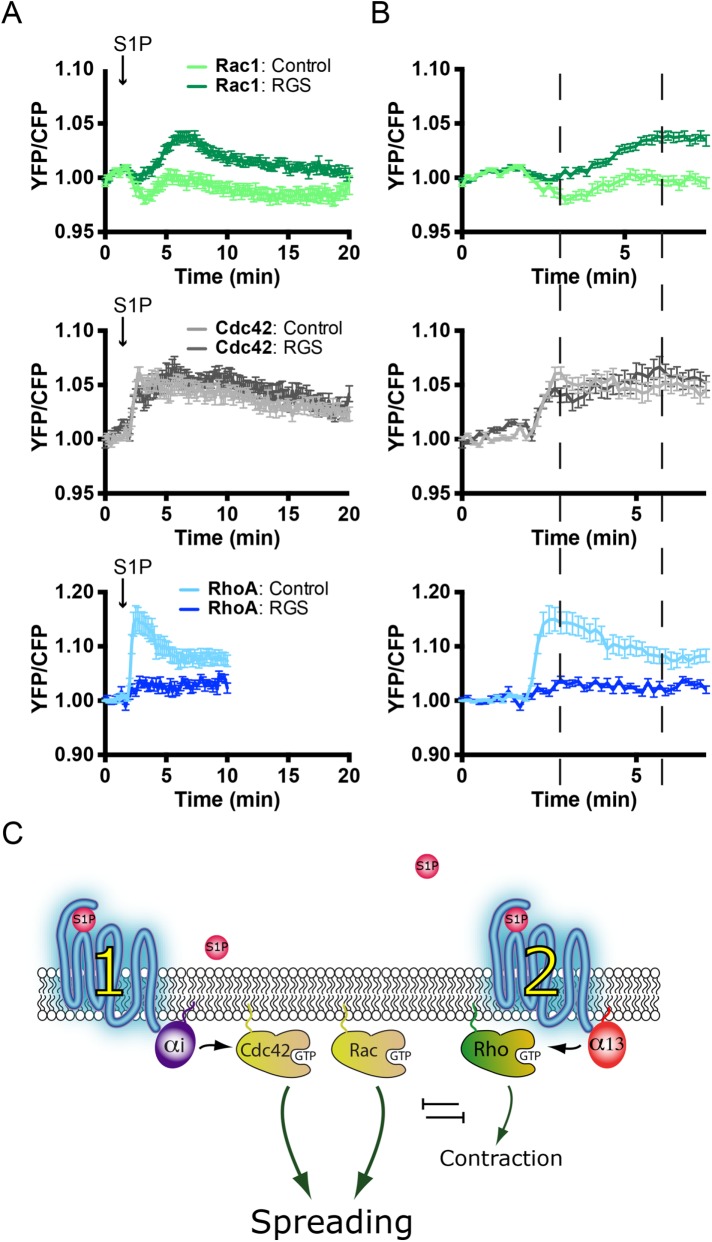
FIGURE 7:
Gα13 inhibition enhances S1P-induced Rac1 activation and blocks RhoA activation. (A) Normalized mean YFP/CFP ratio traces (±SEM) for Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA FRET sensor-expressing ECs before and after stimulation with S1P at t = 1 min, 50 s. FRET sensor–positive ECs coexpress either Lck-mCherry (control) (Rac1, n = 20; Cdc42, n = 21; RhoA, n = 14) or Lck-RGS-mCherry (RGS) (Rac1, n = 27; Cdc42, n = 22; RhoA, n = 14). (B) Enlargement of normalized mean YFP/CFP ratio traces (±SEM) corresponding to the first 7 min of A. Dashed lines highlight maximal and minimal YFP/CFP ratio changes. Note the increased Rac1 activation at ∼7 min and the inhibition of RhoA activation upon coexpression of the RGS domain. (C) Model describing S1P-mediated signaling pathways in ECs. Balancing G-protein and RhoGTPase signaling results in S1P-induced cell spreading, which dominates over the limited RhoA activation and consequent contraction.