Fig. 2.
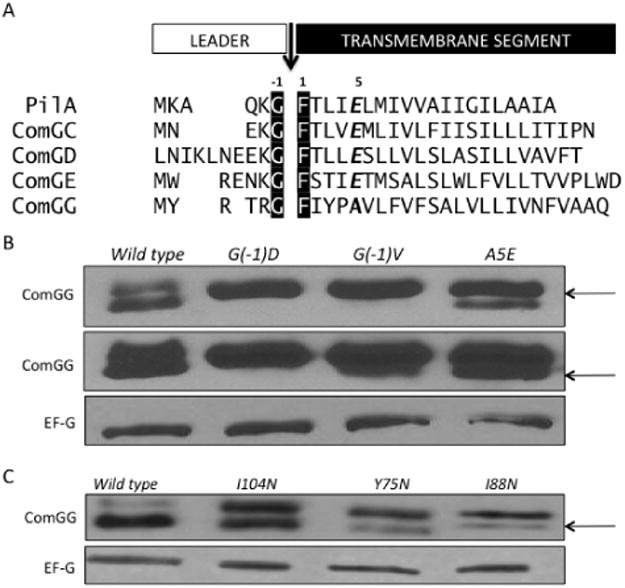
ComGG processing depends on both N- and C-terminal residues.
A. The N-terminal segments of B. subtilis pilin proteins, ComGC, ComGD, ComGE and ComGG, are aligned with PilA of P. aeruginosa. The black arrow denotes the end of the leader sequence with the canonical pilin cleavage motif G/F, highlighted in black. ComGG lacks the conserved glutamate residue at the +5 position of the mature pilin, indicated in bold italics in the other pilins. The residues immediately following the cleavage sites are predicted to be part of the transmembrane segment (Cserzo et al., 1997; Krogh et al., 2001).
B. Representative Western blot of ComGG N-terminal point mutants: G(−1)D (BD5821), G(−1)V (BD5835) and A5E (BD6782). A more exposed ComGG blot is also shown.
C. Representative Western blot for ComGG C-terminal mutants I104N (BD5802), Y75N (BD5804) and I88N (BD5834) identified in a ComGG loss of function screen. EF-G is included as a loading control. The arrows indicate processed ComGG protein.
