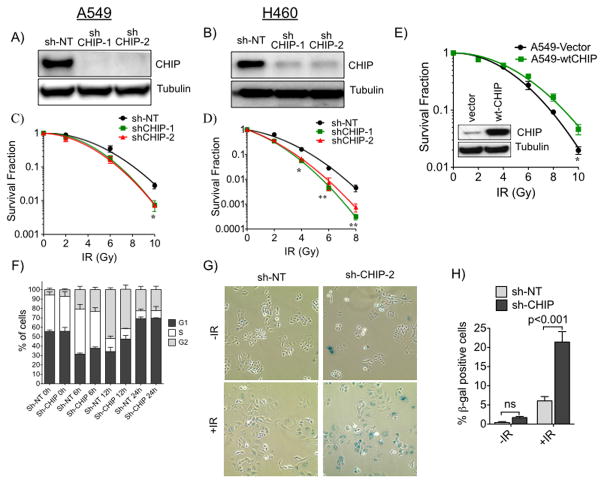
Figure 1.
CHIP dependence of lung cancer cells response to ionizing radiation (IR). A, A549 and B, H460 cells were depleted of CHIP using two different shRNAs (shCHIP-1 & shCHIP-2). Cell lysates were immunoblotted for CHIP and tubulin as loading control. Clonogenic survival of C, A549 and D, H460 cells depleted of CHIP treated with different doses of IR. Survival fractions were fitted to linear-quadratic model. E, Clonogenic survival of A549 cells comparing ectopically expressed WT-CHIP or empty Vector treated and plotted as C or D. Immunoblot of ectopically expressed CHIP (inset). F, FACS analysis of control (sh-NT) and knockdown (sh-CHIP-2) A549 cells harvested at indicated time points after IR (10 Gy). G, CHIP proficient and deficient cells (as F) were treated with or without 10 Gy and cellular senescence was measured 24h after IR by β-gal staining. H, Quantification of senescence cells. Error bars for C–F and H represents the mean ±SD of at least three independent experiments. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.