Figure 6. LASSO-based cloning and characterization of full-length ORFs from human cDNA or DNA isolated from a human microbiome sample.
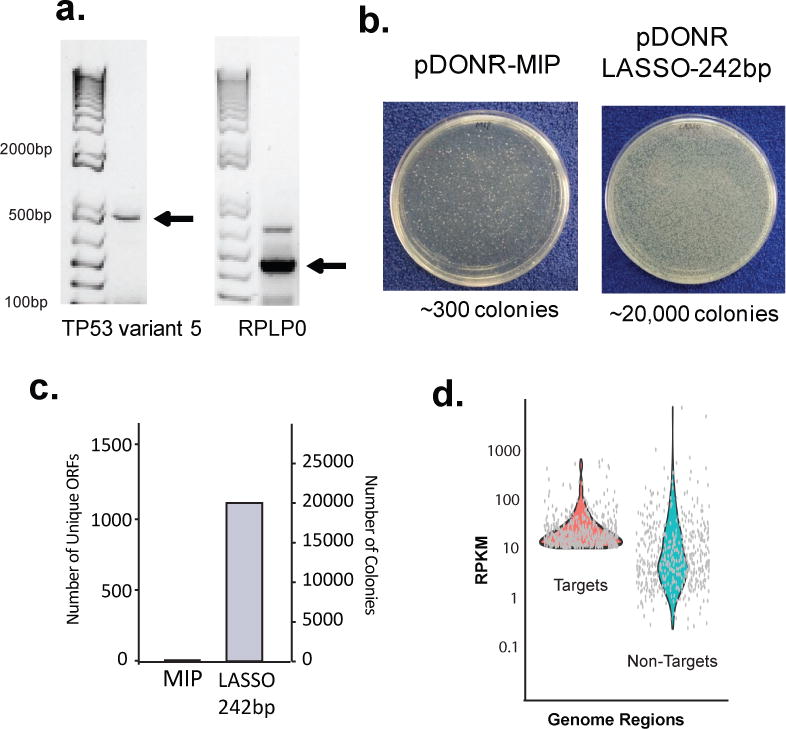
(a) Capture of Human ORFs from a mammalian cDNA library. Post capture PCR of tumor suppressor TP53 variant 5 (783 bp) (left), and housekeeping RPLP0 internal fragment (323 bp) (right) captured from Jurkat E6-1 cDNA. Note there is the addition of 142 bp from linker for each cDNA captured. (b) E. coli colonies transformed with captured ORFs using LASSO-242bp or MIP libraries and cloned into the pDONR211 vector. (c) Number of detected ORFs from LASSO-242bp-pDONR211 and MIP-pDONR211 captured from DNA isolated from a human stool sample. Number of colonies from the transformations as in (b). (d) Average depth of sequencing, analyzed as target reads per kilobase per million reads, for each targeted ORF, or non-targeted genomic region >400 bp. Sequencing depth of top 500 targeted and non-targeted ORFs in the LASSO-242bp-pDONR211 stool DNA-captured library.
