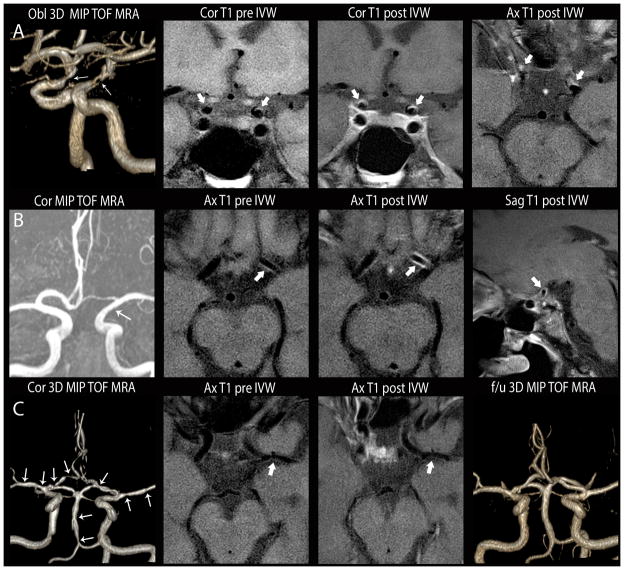
Figure 1.
Comparison of intracranial vasculopathies on luminal imaging and IVWI. A. Atherosclerosis. Oblique 3D MIP 3D TOF MRA (left image) shows irregular narrowing of both supraclinoid ICA (white arrows). Coronal T1 pre-contrast (left middle), coronal (right middle) and axial (right) T1 post-contrast images show irregular, eccentric wall thickening with mild, incomplete lesion enhancement (thick white arrows). B. Inflammatory vasculopathy. Coronal 3D MIP MRA (left) shows subtle diffuse narrowing of the left supraclinoid ICA (white arrow). Axial T1 pre-contrast (left middle), axial (right middle) and sagittal (right) T1 post-contrast IVWI images show circumferential wall thickening with diffuse lesion enhancement (thick white arrows). Subsequent biopsy indicated primary angiitis of the CNS. C. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Coronal 3D MIP TOF MRA (left) of the circle of willis shows multi-focal narrowing involving all arterial territories (arrows). On axial T1 pre- (left middle) and post- (right middle) contrast, there is minimal wall thickening without enhancement of a left MCA lesion (thick white arrow). On follow-up TOF MRA (left) performed 2 months later, multi-focal stenoses had resolved.