Figure 1.
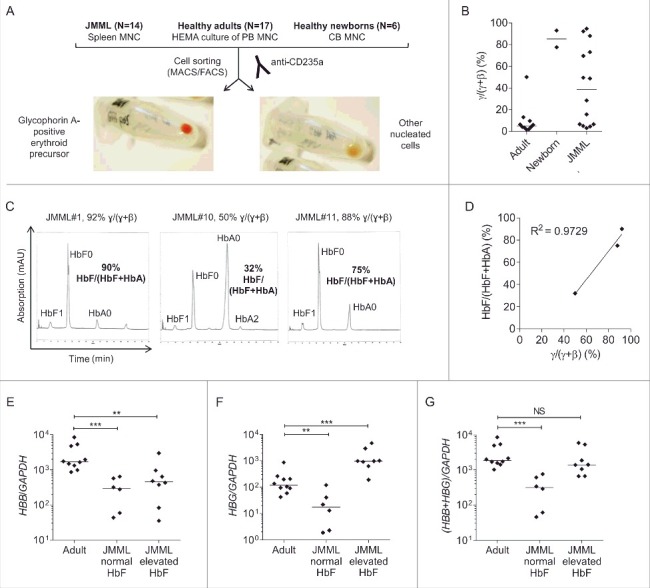
β-like globin expression in glycophorin A-positive erythroid precursor cells. (A) Isolation of GPEP cells and other nucleated cells from cryopreserved spleen cells of JMML patients, in vitro-differentiated blood cells of healthy adults and cord blood cells of healthy newborns. (B) β-like globin mRNA level [γ/(γ+β) mRNA quotient] measured by RT-qPCR in GPEP cells of adults, newborns, and JMML patients. (C) High pressure liquid chromatography to determine hemoglobin variants in GPEP cells of 3 patients with JMML. HbF0/HbA0/HbA2: unmodified, HbF1: glycosylated; for the calculation of %HbF as HbF/(HbF+HbA) the amount of unmodified and glycosylated HbF was considered. For each patient, the corresponding globin mRNA quotient is indicated above the chromatogram. (D) Correlation between globin mRNA quotient and %HbF in GPEP cells of 3 patients with JMML. (E) HBB transcript levels relative to the GAPDH reference gene in GPEP cells of adults, JMML patients classified as normal HbF, and JMML patients classified as elevated HbF. (F) HBG transcript levels relative to GAPDH in GPEP cells of adults, JMML patients classified as normal HbF, and JMML patients classified as elevated HbF. Due to high sequence homology, the assay did not discriminate between HBG1 and HBG2. (G) Total β-like globin transcription relative to GAPDH in GPEP cells of adults, JMML patients classified as normal HbF, and JMML patients classified as elevated HbF. Mann-Whitney test: NS, not significant; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. MNC, mononuclear cells; HEMA, human erythroid massive amplification; CB, cord blood.
