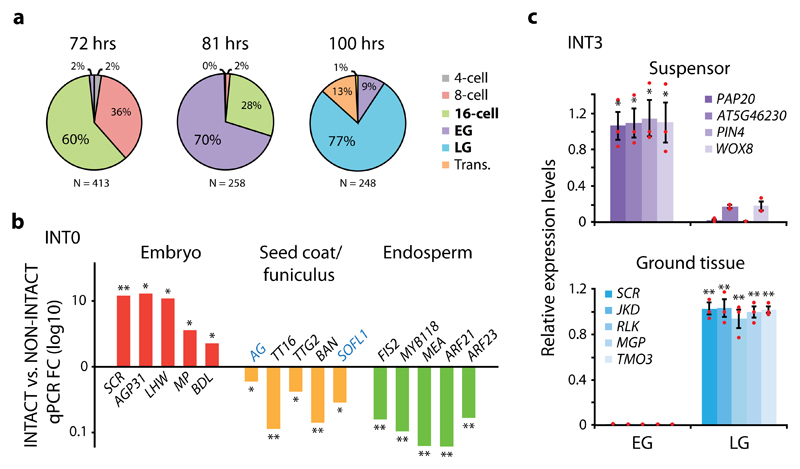
Figure 2. INTACT efficiently isolate cell type- and stage-specific nuclei.
(a) Optimal time intervals in hours (hrs) for the isolation of 16-cell (72 hrs), early globular (EG; 81 hrs) and late globular (LG; 100 hrs) embryonic stages following manual pollination of pWOX2-mBirA-3xMyc plants. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) analysis showing enrichment (FC; fold change) of genes predominantly expressed in embryo, seed coat, seed coat/funiculus (blue text) or endosperm when comparing INT0 (whole) embryo-derived nuclei (INTACT) to total seed nuclei (NON-INTACT). (c) qPCR relative expression levels of genes predominantly expressed in the suspensor or ground tissue in nuclei derived from the INT3 line, where pOFP8-NTF is expressed first in the suspensor at EG and then primarily in the ground tissue at LG. Suspensor- and ground tissue-expressed genes show enrichment in EG and LG, respectively. Results are based on mean values and SEM of 3 biological replicates in both b and c. In c, individual data points are plotted as red dots. Asterisks denote significance levels (*p <0.05, **p <0.01) as determined by one-tailed Welch’s t-test. Normal distribution is assumed.