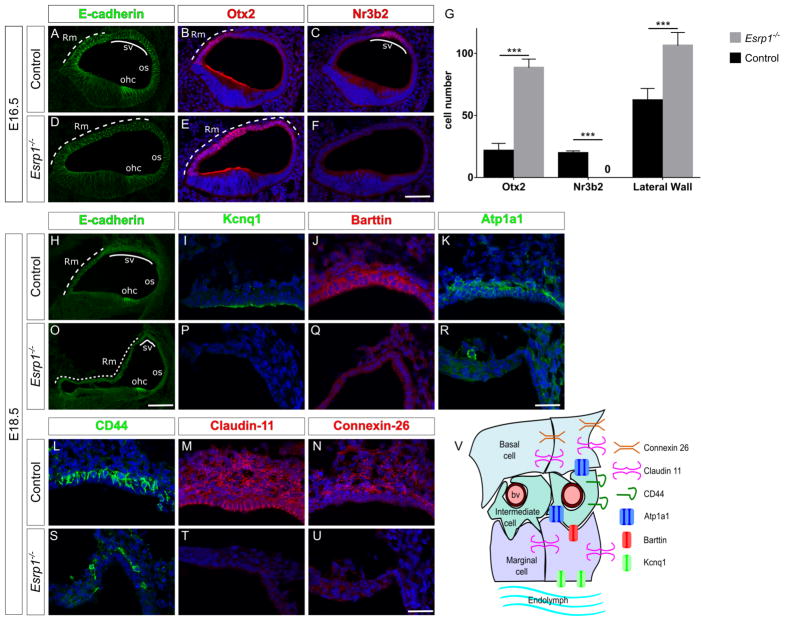
Figure 5. Esrp1 regulates the identity of nonsensory cells along the lateral cochlear wall.
(A–F) Transverse sections through the cochlear duct of control (n=8) and Esrp1−/− (n=6) embryos at E16.5 immunostained for E-cadherin (A,D), Otx2 (B,E) and Nr3b2 (C,F). (G) Quantification of cells expressing Otx2, Nr3b2, as well as the total number of cells in the lateral cochlear epithelium represented as mean ± SD (***P<0.0001, Student’s t-test). (H–U) Transverse sections through the cochlear duct of control (n=5) and Esrp1−/− (n=5) embryos at E18.5 immunostained for E-cadherin (H,O), and indicated cell type specific markers of the stria vascularis (I–N, P–U). Scale bar = 50μm (A–F, H,O) and 25μm (I–N, P–U). (V) Schematic of the stria vascularis displaying cell types and markers analyzed in (H–U). Abbreviations: blood vessel (bv), outer hair cells (ohc), outer sulcus (os), Reissner’s membrane (Rm) and stria vascularis (sv). See also Figure S6 and Table S2.