Figure 4. Signal transduction by the Gibberellin receptor (GID1).
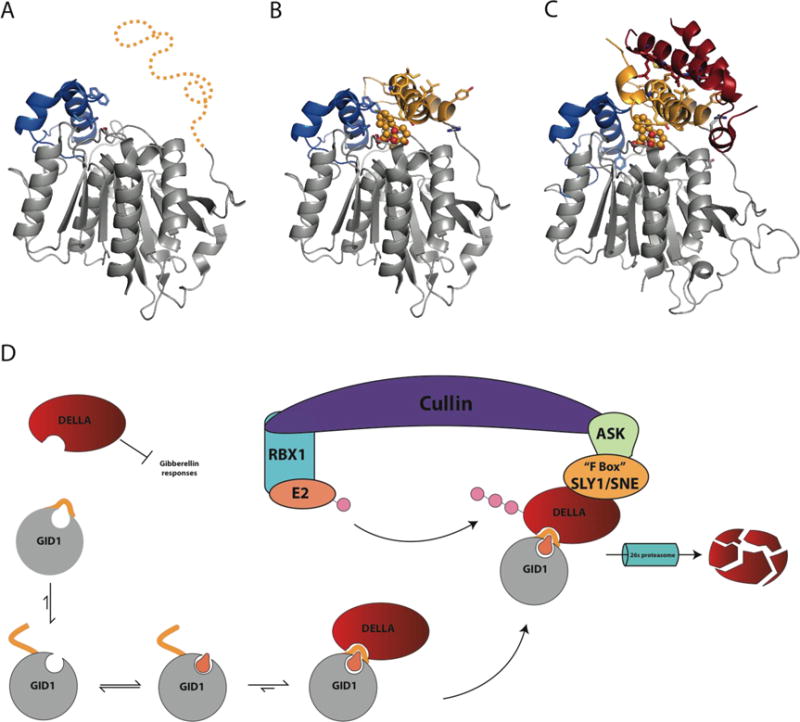
A) Proposed Apo GID1 structure (3EBL with ligand deleted) of flexible N-terminal lid region (Gold) from OsGID1 before becoming ordered due to substrate binding (PDB 3EBL). B) Crystal structure of OsGID1A in complex with gibberellin (GA4) covered by N-terminal lid region. Solvent exposed hydrophobic residues on the N-terminal lid are shown in stick (PDB 3EBL). C) Complex formed between AtGID1 and the helical N-terminal DELLA domain of GAI (red). Residues involved with the recognition and interaction between GID1 and GAI are shown as stick and colors correspond to their respective structures (red, DELLA; Gray/Gold, GID1) (PDB 2ZSI). D) The regulation of gibberellin hormone signaling by DELLA proteins and the GID1 receptor. Upon binding GA, the N-terminal region orders itself over the GA binding site, providing an interaction site for DELLA proteins. GID1-DELLA complex is then recruited to an SCF(SKP1-like Cul1 F-box) E3 ubiquitin-ligase complex, which is comprised of Cullin, the RING-H2 protein RBX1, a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2, and an SKP1-like protein that acts as a substrate adaptor to recruit specific FBOX proteins. FBOX proteins are named for their 50 amino acid FBOX domain and are responsible for recruiting E3 ligase substrates destined for 26s proteasomal degradation through polyubiquitinylation.[61] After recruitment of the GID1-DELLA complex to the SCF complex by SLY1/SNE, DELLA proteins are polyubiquitinylated and destroyed by the 26s proteasome, releasing GA signaling inhibition, allowing transcription of genes under GA control.
