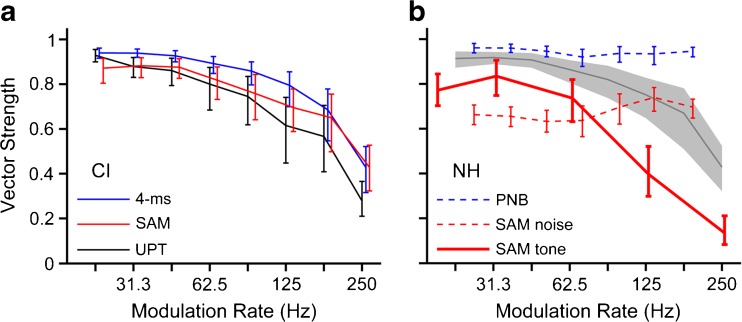
FIG. 6.
Electrical stimulation produces comparable phase locking between modulated high-rate pulse trains and unmodulated low-rate pulse trains and produces stronger phase locking than acoustic stimulation with pure SAM. a Firing rate-weighted mean vector strength as a function of modulation rate for all CI-stimulated neurons in this study. Red line, pure SAM stimulation (diagonal of envelope shape triangle, inset, N = 121). Blue line, narrowest burst width (4 ms, base of envelope shape triangle, N = 121). Black line, unmodulated pulse trains (N = 65). b Comparison to IC responses in NH cats using acoustic stimulation. Gray line: weighted mean vector strength combined across CI responses to pure SAM and 4-ms bursts. Thick red line: pure SAM of tone carrier (N = 92). Dotted red line: pure SAM of a noise carrier, and dotted blue line: trains of 250-μs periodic noise bursts (PNB) (N = 135, Zheng and Escabí 2013). Error bars and gray shading: 95 % confidence intervals based on bootstrap analysis.