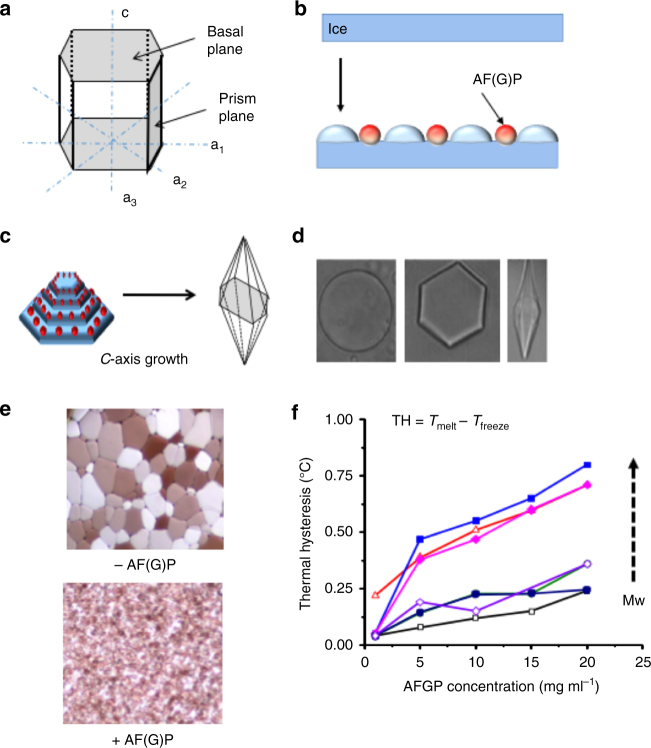
Fig. 2.
Interaction of antifreeze proteins with ice. a Hexagonal ice crystal; b Adsorption-inhibition where AF(G)Ps bind to ice, causing local curvature and hence growth inhibition; c Preferential c-axis (basal) growth when prism planes inhibited; d Different morphologies observed for single ice crystals; e Micrographs of ice crystals after annealing with/without antifreeze proteins showing IRI activity; f TH activity for different molecular weight AFGPs (2.6–24 kDa)4, 33. a–d are reproduced from Gibson (2010)24 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry. These images are not included under the creative commons licence for this article. f was created using the raw data from Wu et al. (2001)33