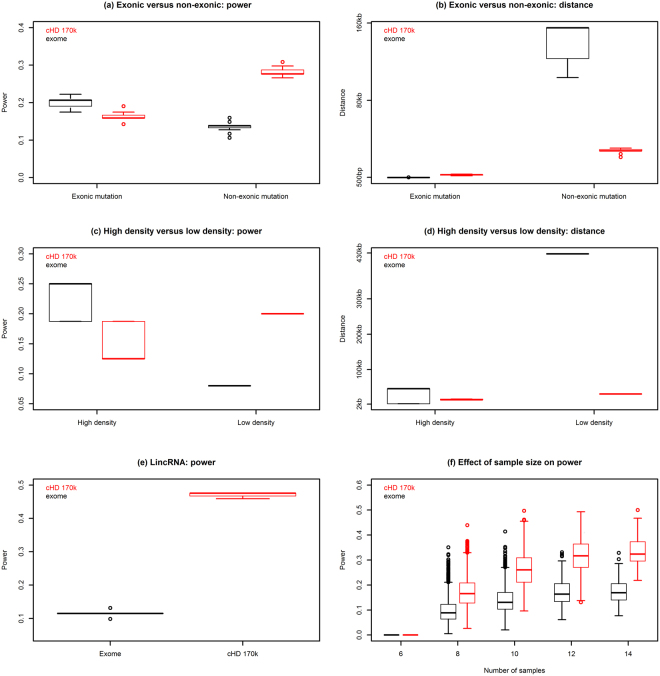
Figure 4.
Power and distance between causal and tagSNPs for the exome-1.0 and canine high-density 170k array. (a) Boxplots showing the power to detect the association when a signal is located inside the target regions and outside the target regions. (b) Boxplots showing distance between the most significant SNP and the causal SNP when the signal is located inside or outside the target regions, respectively. (c,d) Boxplots showing power and distance to detect a non-exonic signal inside WES bins with a high informative SNP density (corresponding to the 85th percentile or higher, threshold: ≥48 SNPs/Mb) and a low informative SNP density (corresponding to at most the 15th percentile, threshold: ≤4 SNPs/Mb). (e) Boxplots showing power to detect a signal in long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs). (f) Effect of sample size reduction on power to detect a monogenic recessive trait. Subsampling was performed stepwise, from 14 down to 6 samples and for each step, at least 20% of all possible permutations of samples were performed. The bottom and top of the boxplot represent the first (Q1) and third quartile (Q3), while the horizontal line in the boxplot represents the median. Whiskers represent 1.5 times the interquartile range (Q3-Q1).