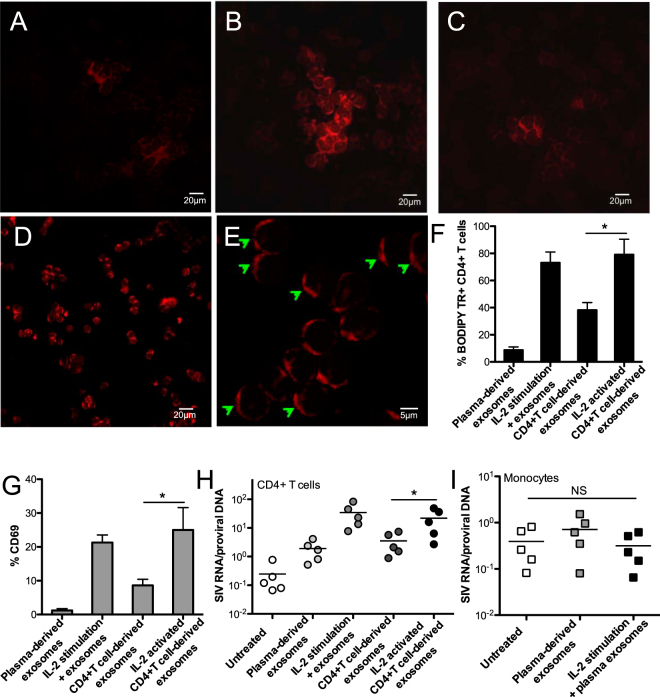
Figure 3.
Autologous exosome uptake by CD4+ T cells, and its effects on reactivation of resting CD4+ T-cells from SIV-infected macaques. Confocal image analysis of exosome fusion to PBMCs, in which PBMCs were incubated by BODIPY TR-labeled plasma exosomes only (A, 20 μm), CD4+ T cell-derived exosomes in presence of IL-2 in media (B, 20 μm), CD4+ T cell-derived exosomes only (C, 20 μm), or exosomes which were isolated from supernatants of IL-2-activated CD4+ T cells (D, 20 μm; E, 5 μm); (F) Percentage of BODIPY TR positive CD4+ T cells that internalize BODIPY TR-labeled exosomes; (G) Activation of CD4+ T cells after exposure to exosomes. PBMC and plasma were isolated from SIV naïve animals, and further CD4+ T cells were isolated and cultured for exosome preparation. Effects of exosomes on viral transcription rate in resting CD4+ T cells (H) or monocytes (I) from chronically SIVmac251-infected macaques. Levels of cell-associated SIV DNA and RNA were measured after 24 hours. Significance determined by a Wilcoxon signed rank test. *P < 0.05. Error bars represent means ± SE.