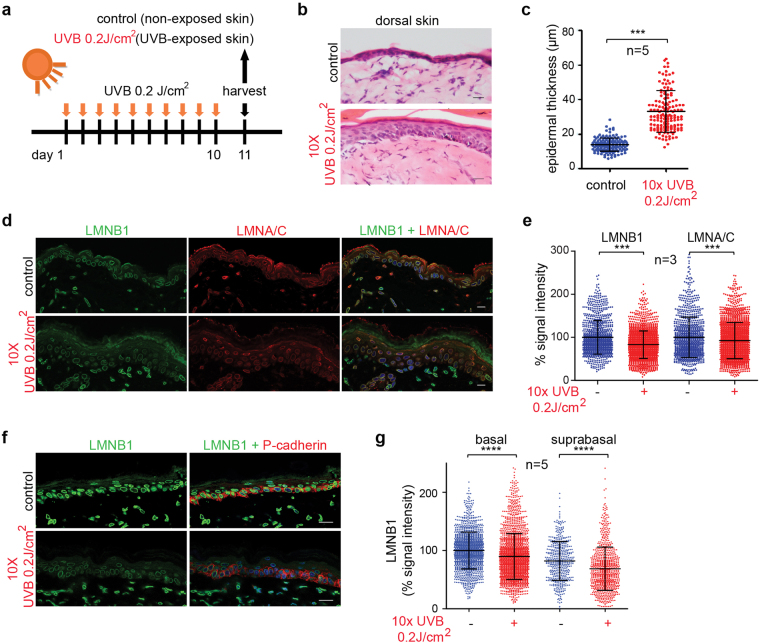
Figure 2.
Chronic UV-exposure results in lamin B1 reduction in mouse skin. (a) Experimental set-up. (b) H&E staining of UV-exposed versus control skin. (c) Quantification of epidermal thickness (n = 5). (d) Immunofluorescence analysis of lamin B1 and lamin A/C expression (LMNB1; green, LMNA/C; red). Bars, 20 µm. (e) Quantification of LMNB1 and LMNA/C levels throughout the epidermis, normalized to non-irradiated controls. n = 3, ***P < 0.001. (f) Immunofluorescence analysis of lamin B1 expression (LMNB1; green, P-cadherin; red). Bars, 20 µm. (g) Quantification of LMNB1 in basal and suprabasal layers, normalized to LMNB1 intensity of non-irradiated basal cells; n = 5, all graphs show mean ± SD, ****P < 0.0001).