Fig. 6.
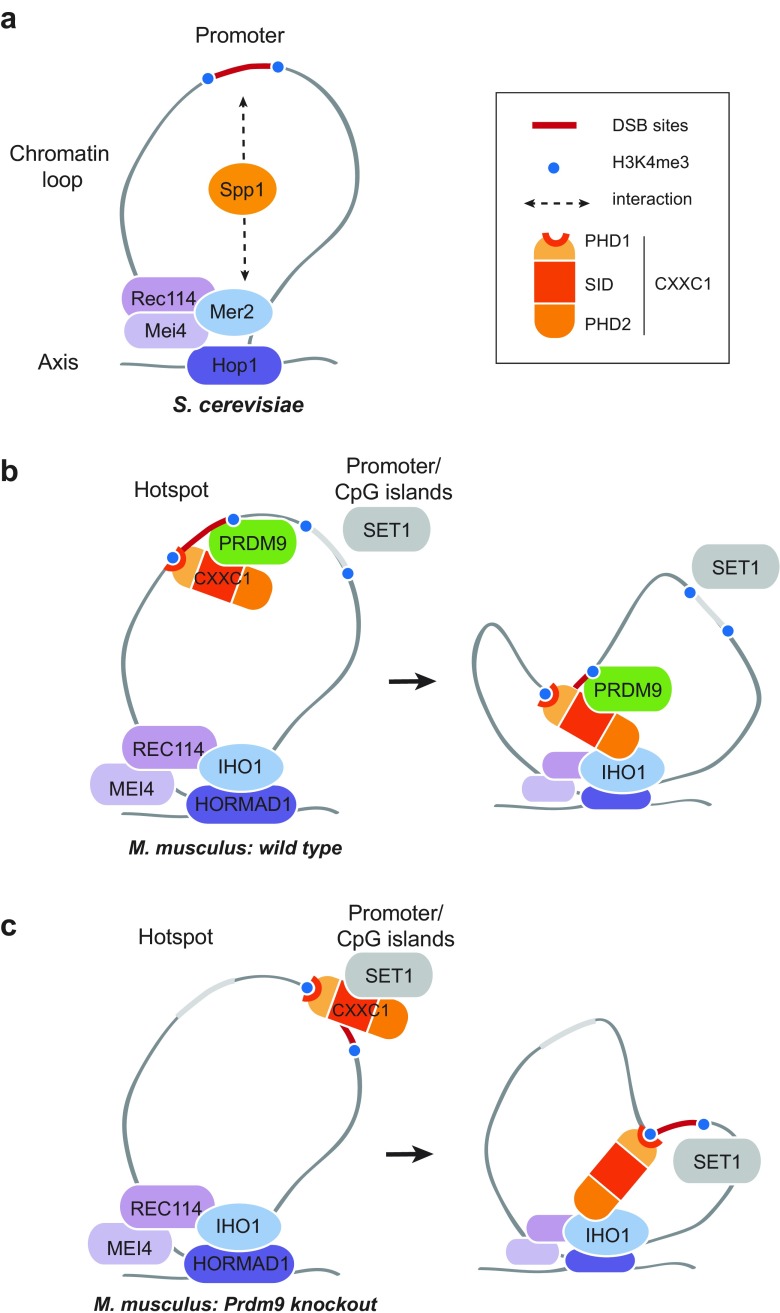
A model of the meiotic function of PRDM9 and CXXC1 in mouse meiosis. a In S. cerevisiae, Spp1 links hotspots to the Rec114-Mei4-Mer2 (RMM) complex through interactions with H3K4me2/me3 and Mer2 during meiosis (Acquaviva et al. 2013; Sommermeyer et al. 2013). The RMM complex axis localization is Hop1-dependent (Blat et al. 2002; Panizza et al. 2011). In this panel and in the following ones, only one sister chromatid is drawn. The other sister chromatid may or not be associated and involved in these interactions. b At leptonema in wild-type mouse meiosis, CXXC1 is not associated with SET1 but interacts with the KRAB domain of PRDM9 through its SID. In addition, CXXC1 interacts with H3K4me3 deposited by PRDM9 via PHD1 and can interact with IHO1 via PHD2. These interactions facilitate the recruitment of hotspots to the DSB machinery on chromosomal axes. c In Prdm9 knockout mice, CXXC1 could be associated with promoters/CpG islands similarly to the localization reported in somatic cells (Thomson et al. 2010). This association may involve interaction with SET1, H3K4me3, and DNA-binding through the CXXC zinc finger. CXXC1 and IHO1 interact leading to DSB formation near promoter/CpG islands (Brick et al. 2012)