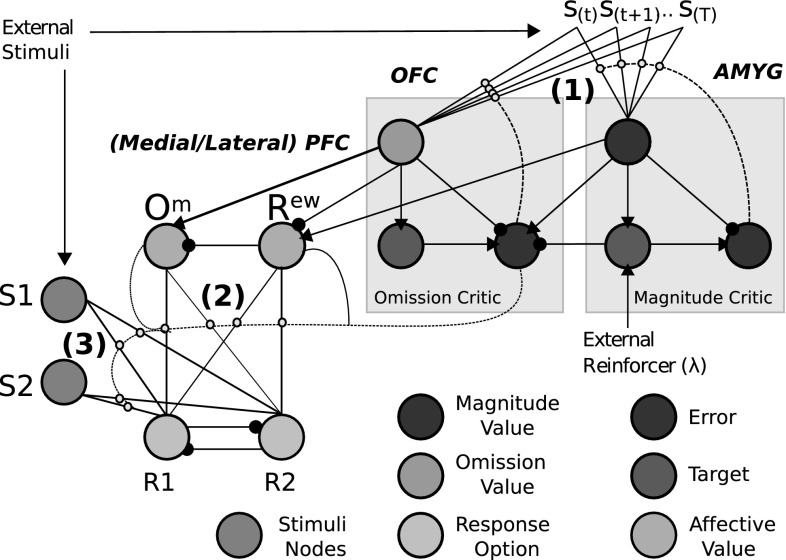
Fig. 8.
Affective–associative two-process network. Our associative–affective component builds on Trappenberg’s and Balkenius and Morén’s (2001) neural network models. It further adds an ‘actor’ whereby the outputs of the two ‘critic’ value dimensions become associated with response options. Mutual inhibition promotes dimensional mediation of responses. The computations of individuals nodes are derivable according to Fig. 7 and Eqs. (1–12). Small yellow circles indicate learnable connections (gated by prediction error value). S1/S2 connections to R1/R2 provide the ‘retrospective’ (S–R; label 3) route of ATP. The Om and Rew connections to R1/R2 provide E–R connections (2). Finally the S(t) inputs here provide temporal stimulus valuations and allow for S–E connections (1). Key: OFC orbitofrontal cortex, AMYG amygdala, PFC prefrontal cortex (colour figure online)