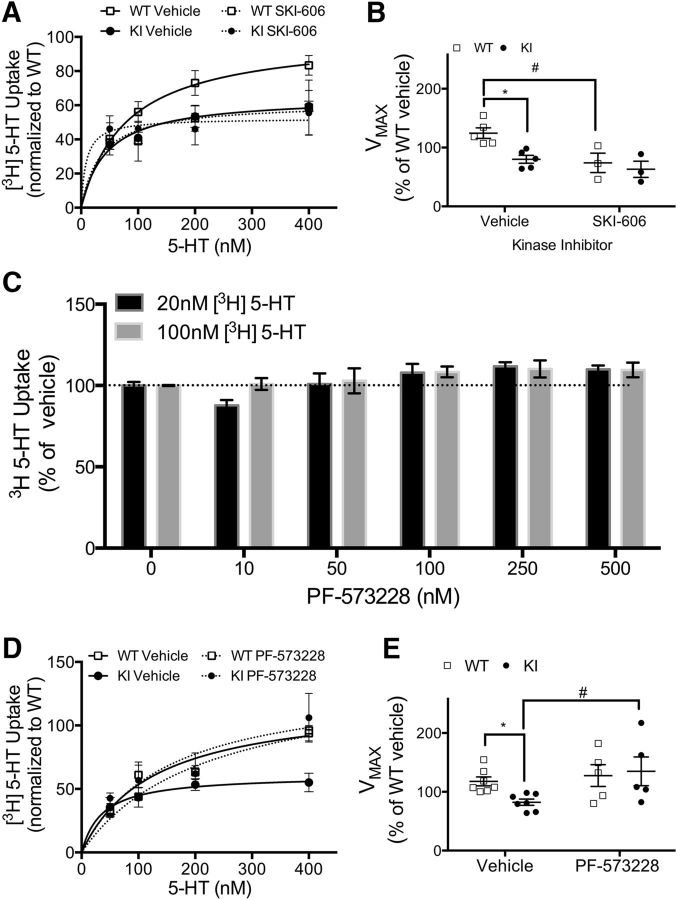
Figure 5.
Inhibition of FAK, but not Src, rescues SERT activity in KI mice. Representative kinetic saturation curves of SERT-mediated [3H] 5-HT uptake in WT (□) and KI (■) midbrain synaptoneurosomes treated with vehicle (solid lines) or kinase inhibitors (dashed lines). A, Representative curves for samples treated with vehicle or the Src inhibitor SKI-606 (100 nm). B, Analysis of maximum SERT-mediated 5-HT transport velocity (Vmax) from kinetic saturation experiments in samples treated with vehicle or SKI-606 (two-way ANOVA SKI-606 effect: F(1,12) = 7.36, p = 0.019; two-way ANOVA genotype effect: F(1,12) = 5.53, p = 0.036; Bonferroni-corrected post-test: WTvehicle vs KIvehicle, p = 0.019; WTvehicle vs WTSKI, p = 0.026). Number of animals: WT, Nvehicle = 5, NSKI = 3; KI, Nvehicle = 5, NSKI = 3. C, Concentration-response analyses of the FAK inhibitor PF-573228. SERT-mediated [3H] 5-HT uptake (20 and 100 nm) in WT synaptoneurosomes was measured in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of PF-573228. Number of animals, 8. D, Representative curves for samples treated with vehicle or the FAK inhibitor PF-573228 (100 nm). E, Analysis of maximum SERT-mediated 5-HT transport velocity (Vmax) from kinetic saturation experiments in samples treated with vehicle or PF-573228 (100 nm; two-way ANOVA PF-573228 effect: F(1,20) = 5.05, p = 0.036. Bonferroni-corrected post-test: KIvehicle vs KIPF, p = 0.029). Number of animals: WT: Nvehicle = 7, NPF = 5; KI: Nvehicle = 7, NPF = 5. For genotype comparisons: *p < 0.05, and drug comparisons within the same genotype; #p < 0.05.