Fig. 9.
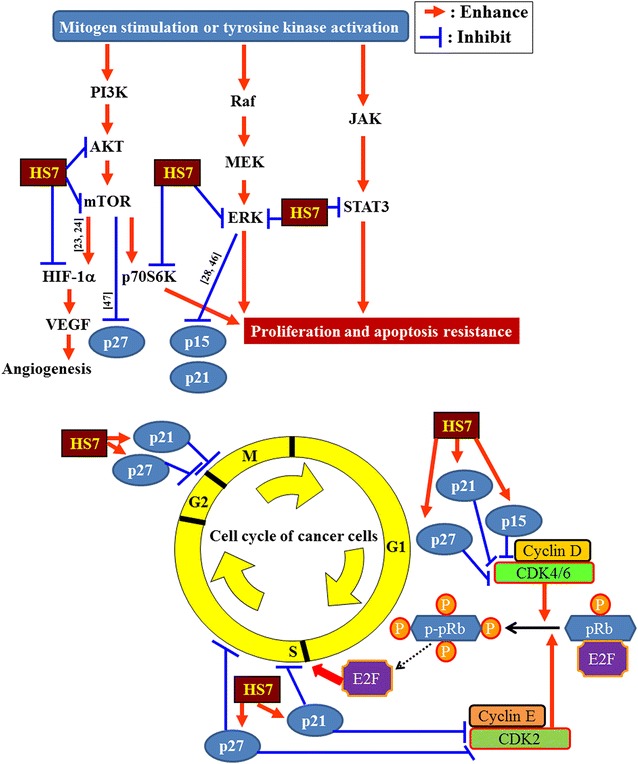
Schematic diagram displays the proposed mechanisms of action of HS7 in CL1-0 lung cancer cells. Through inhibition of AKT-mTOR, ERK and STAT3 signaling pathways, the active fraction HS7 from T. camphoratus increases the CDK inhibitors (p15, p21 and p27) and leads to cell cycle suppression and apoptosis induction. References for the proposed inhibition or enhancement are indicated along the arrow or T-bar. ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinases, HIF-α hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, JAK Janus kinase, MEK mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, p70S6K ribosomal p70 S6 kinase, PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase, Raf rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
