Fig. 3.
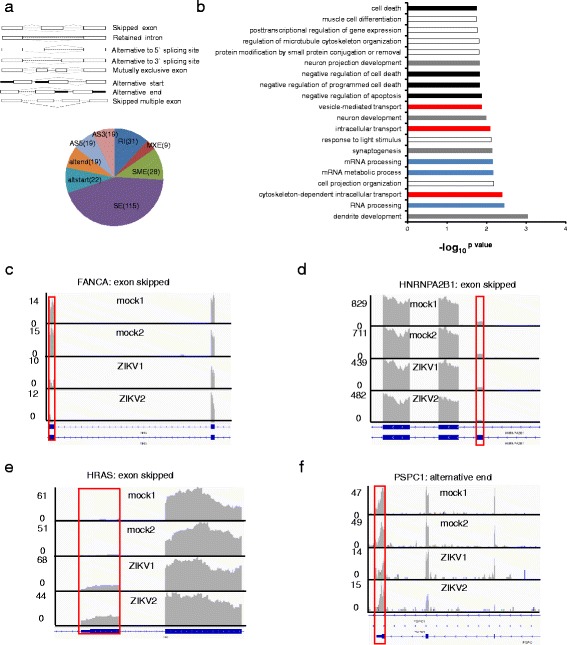
ZIKV infection induced alternative splicing of the cellular transcriptome. a. 262 significant differentially AS cases occurred 229 significant alternative splicing genes were detected, which falls into skipped exon, skipped multiple exon, alternative to 5′splicing site (AS5), alternative to 3′splicing site (AS3), alternative start (altstart), alternative end (altend), mutually exclusive and retained intron classes [16]; b. GO analysis of AS genes, the x-axis is the –log10 p value, Black, gray, read, and blue denotes cell death, neuron development, transport, and RNA processing, respectively; c–k. Visualization of alternative splicing. Y-axis shows the number of mapped reads. c. FANCA: increased SE after infection; d. HRAS: increased exon after infction; e. HNRNPA2B1: reduced exon after infection; f PSPC1: reduced altend after infection
