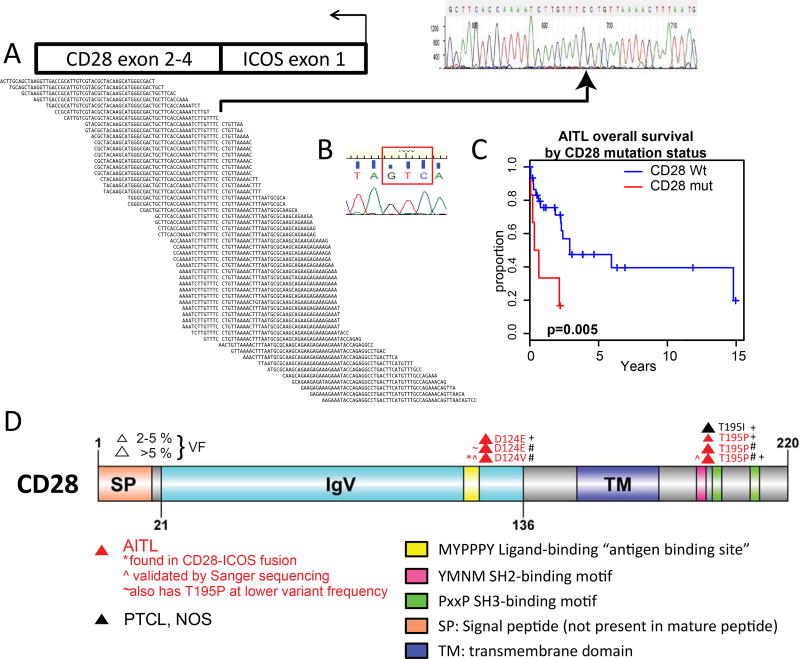
Figure 1. Distribution of CD28 mutations discovered on transcriptome and targeted sequencing in T-cell lymphoma subtypes.
A: Alignment of ICOS-CD28 fusion transcript and identification of breakpoint, verified by Sanger sequencing. B: Demonstration by Sanger sequencing of D124V mutant in ICOS-CD28 transcript, GAC>GTC (red box). C: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of AITL cases with CD28 mutations (red) versus AITL cases with no CD28 mutations (black). CD28-mutant cases had inferior survival after diagnosis (p=0.005). D: CD28 map and mutations found in 20 AITL cases with whole transcriptome sequencing plus 38 AITL (including five cases overlapping with transcriptome sequencing; red), 40 PTCL-NOS (black), and 12 ALK-ALCL cases. SP: signal peptide; IgV: Ig variable region-like domain CD28 and CTLA4; TM: transmembrane domain. Yellow: “antigen-binding” site required for interaction with ligand within IgV domain; pink: SH2-binding motif; green: SH3-binding motifs. #: identified in whole-transcriptome sequencing; +: identified in targeted sequencing platform. The diagram was built using DOG, version 2.060.