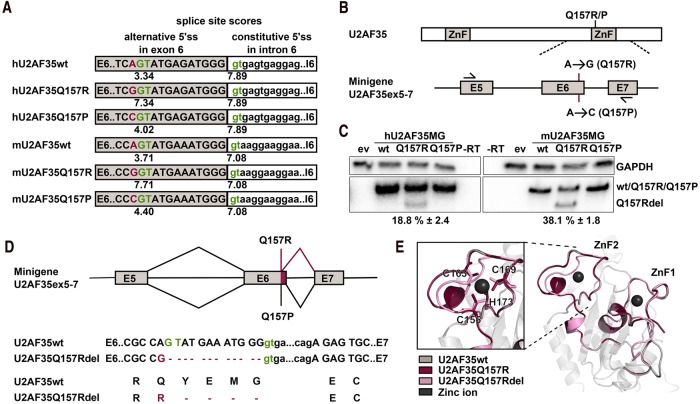
FIGURE 1.
The U2AF35 Q157R mutation creates an alternative 5′ splice site. (A) Sequences of the exon 6 to intron 6 junction of human and mouse U2AF35. Constitutive and potential alternative donor splice sites are shown in green and nucleotides encoding AML-associated substitutions Q157R/P are shown in red. The numbers below the donor sites show the splice site scores. (B) Schematic depiction of minigene constructs spanning introns 4–8, including exons 5–7, and the introduced point mutations. (C) Minigene-specific, radioactive splicing-sensitive RT-PCR and quantification using HEK293T cells transfected with human and mouse U2AF35 minigenes or the empty vector (ev). GAPDH-specific radioactive RT-PCR was used as the loading control. (D) Schematic depiction of the splicing pattern of minigenes with the Q157R and Q157P mutation. Sequences of the exon 6 to exon 7 junction of wt U2AF35 and U2AF35 Q157Rdel and the translated proteins are shown. (E) Structure prediction of U2AF35wt, Q157R, and Q157Rdel with the coordinated zinc ions. The zoom on ZnF2 shows the zinc-coordinating cysteine and histidine residues as sticks.