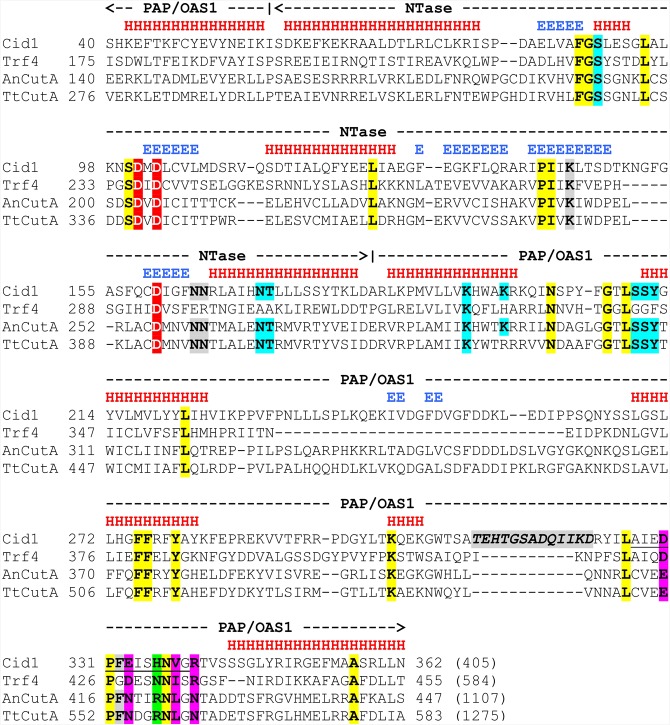
FIGURE 1.
Multiple sequence alignment of the catalytic (NTase) and central (PAP/OAS1 SBD) domains from S. pombe Cid1 poly(U) polymerase, S. cerevisiae Trf4 poly(A) polymerase, and CutA proteins from A. nidulans (AnCutA) and T. terrestris (TtCutA). Domain ranges are shown above the alignment with dashed lines ending with arrowheads. Locations of observed secondary structure elements in Cid1: α-helices and β-strands are marked with red “H” and blue “E” letters, respectively, above its amino acid sequence. Three conserved aspartates in the active site are highlighted in red. H336, primarily responsible for UTP selectivity of Cid1, and corresponding amino acids in other proteins are marked with green. Other residues within or in the vicinity of the nucleotide recognition motif (NRM), including those that were subjected to mutations in our study, are highlighted in magenta. Amino acids from other parts of the protein, involved in NTP recognition, are marked with blue. Remaining residues important for nucleotidyltransferase activity are highlighted in gray (β-trapdoor loop, unique for Cid1, is additionally marked with italics). Cid1 NRM (residues 327–339) is underlined. Other highly evolutionary conserved amino acids are indicated in yellow.