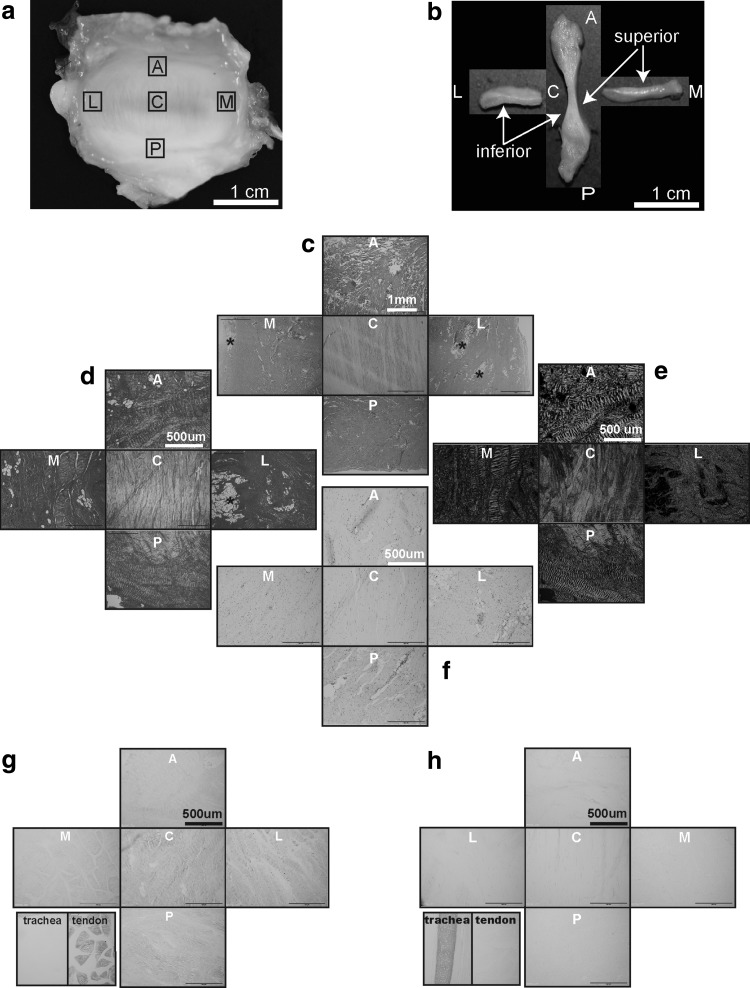
FIG. 1.
Gross morphology, cross sectional parameters, histology, histochemistry, and immunohistochemistry of the minipig TMJ disc. Capital letters represent anatomic regions of the disc: A, anterior; C, central; L, lateral; M, medial; P, posterior. (a) Superior surface view of the whole intact normal minipig TMJ disc. (b) Minipig TMJ disc sectioned in the anteroposterior and mediolateral directions demonstrating a biconcave morphology. (c) Representative horizontal hematoxylin and eosin sections from five anatomic regions of the minipig TMJ disc (scale bar = 1 mm). This panel demonstrates (1) distinct and an almost exclusively anteroposterior orientation of the collagen fibers in the central region and (2) fiber orientation primarily perpendicular to the sectioning plane in the lateral, medial, and posterior regions. Occasional small adipose tissue islands (*) are present in the lateral and medial regions of the disc. (d, e) PicroSirius Red staining of the horizontal disc sections highlights the previously described collagen fiber orientation and crimping of the collagen fibers viewed under regular and polarized light, respectively. (f) Safranin O/Fast Green staining of the horizontal disc sections demonstrates very faint positive staining for GAGs in all disc regions. (g) Collagen type I immunolabeling performed on the horizontal sections of the disc demonstrates diffused immunopositivity across all disc regions. Negative tissue control (trachea) demonstrates no immunopositivity, while positive tissue control (tendon) is immunoreactive for this antigen. (h) Collagen type II immunolabeling performed on the horizontal sections of the disc demonstrates minimal immunoreactivity for collagen type II in all disc regions. The positive tissue control (trachea) is strongly immunoreactive, while negative tissue control (tendon) shows no immunoreactivity. GAGs, glycosaminoglycans; TMJ, temporomandibular joint.