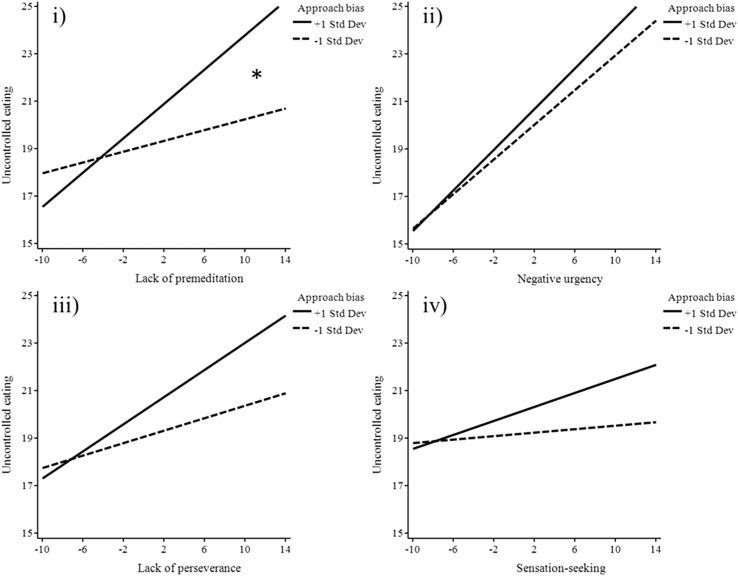
Fig. 1.
Graphical representation of separate impulsivity factors at high and low levels of approach bias for food predicting uncontrolled eating (i) lack of premeditation x food bias was the only significant interaction, (ii) negative urgency x food bias, (iii) lack of perseverance x food bias, (iv) sensation-seeking x food bias were non-significant interactions.