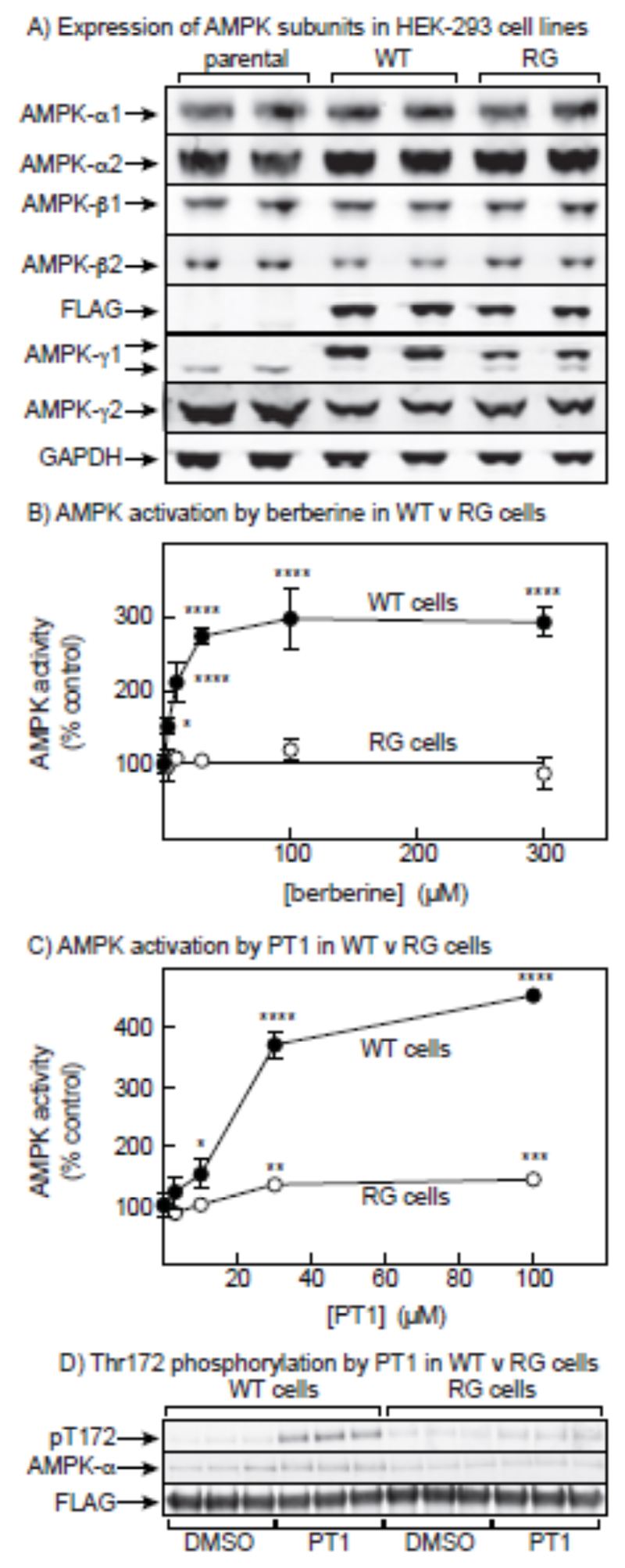
Figure 5.
PT-1 fails to fully activate AMPK in a cell line expressing an AMP-insensitive AMPK-γ1 mutant. (A) Characterization by Western blotting of parental HEK-293 cells and cells stably expressing either the wild type (WT) or the R299G mutant (RG) of AMPK-γ1. Duplicate cell lysates were blotted with the indicated antibodies. (B) Effect of incubating WT or RG cells with increasing concentrations of berberine for 1 hr. AMPK was immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG antibody and immunoprecipitates assays for AMPK activity. Results are expressed as % of the activity in a control without berberine. Mean values significantly different from controls without berberine (1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, n = 4) are indicated: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. (C) As (B), but replacing berberine by PT-1 (n = 3). (D) Effect of PT-1 (n = 3) on phosphorylation of Thr172; Western blots for total AMPK-α and FLAG are also shown to confirm equal loadings.