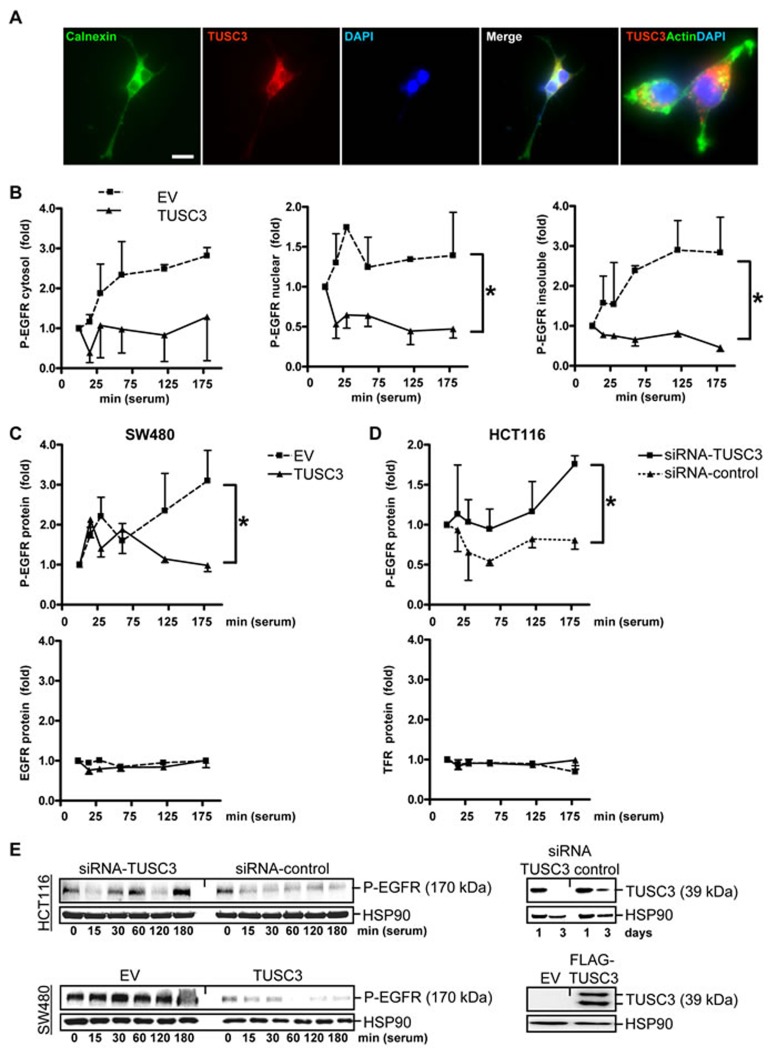
Figure 2. TUSC3 inhibits EGFR phosphorylation.
A., Subcellular localization of ectopic TUSC3 protein at the ER. SW480 cells were transfected with FLAG-TUSC3 plasmid, fixed and stained for immunofluorescence microscopy. Color legend: red = FLAG-TUSC3, green = calnexin (ER marker) or phalloidin (actin), blue = nuclei (DAPI). Overlay of TUSC3 with calnexin or actin appears in yellow. Magnification 630x. B., TUSC3 blocks tyrosine phosphorylation of EGFR/Her1. SW480 cells were transfected with TUSC3 and EV plasmids for 24 h, followed by serum removal (“starvation”) for 16 h and a restimulation with 20 % FCS (“serum shock”) for 0 to 3 h before cell harvest. Cells were then subjected to subcellular fractionation (SCF). Western blot analyses were done with an Ab against the C-terminal cytoplasmic (intracellular) domain containing phospho-tyrosine residue Y1068 important for EGFR activity (P-EGFR). O.D. values from bands in gels were calculated as -fold ± S.E. (*p < 0.05 TUSC3 vs. EV, Two-way ANOVA, n = 3). C., TUSC3 inhibits EGFR phosphorylation without affecting total cellular EGFR protein levels. Cells were transfected and treated as in B and total cell lysate (TCL) was subjected to Western blot using the C-terminal Ab against the phosphorylated (Y1068) (*p < 0.05 TUSC3 vs. EV, Two-way ANOVA, n = 3) and unphosphorylated intracellular domain of the EGFR (n.s.). Data are calculated as in B. Similar results were obtained for the transferrin receptor (TFR/CD71). D., TUSC3 knock-down increases EGFR phosphorylation. HCT116 cells were transfected with siRNAs and analyzed for P-EGFR in TCL as in B (*p < 0.05 TUSC3-siRNA vs. control-siRNA, Two-way ANOVA, n = 4). E., Representative Western blots of the experiments in C-D are shown.