Figure 7. G83D induces genomic instability and mutagenesis.
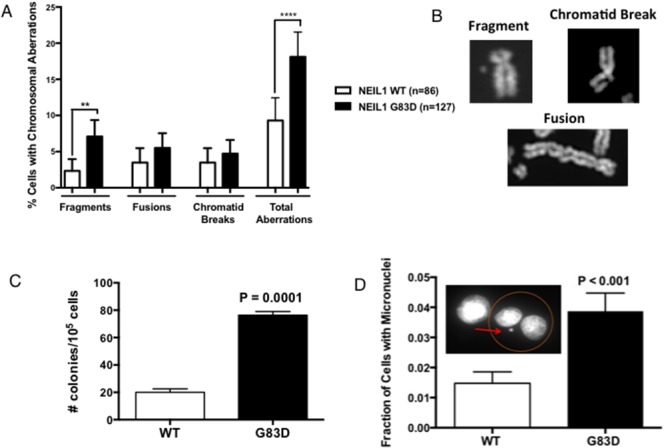
(A) Assessment of chromosomal aberrations. Experiments were performed as described in methods using cells at passage 2. Expression of the G83D variant induces significantly increased numbers of fragments and total aberrations compared to WT. At least 50 nuclei were analyzed. ** p=0.007; **** p < 0.0001. (B) Examples of types of chromosomal aberrations scored in the assay. (C) Determination of mutagenic potential. Oubain resistance was scored in cells at passage 2 as described in methods. Expression of G83D induces point mutations at a significantly increased frequency over that of WT. (D) Measurement of micronucleus formation. Micronuclei were scored as described in methods. The G83D cells exhibit significantly increased levels of micronuclei when compared with WT NEIL1-expressing cells.
