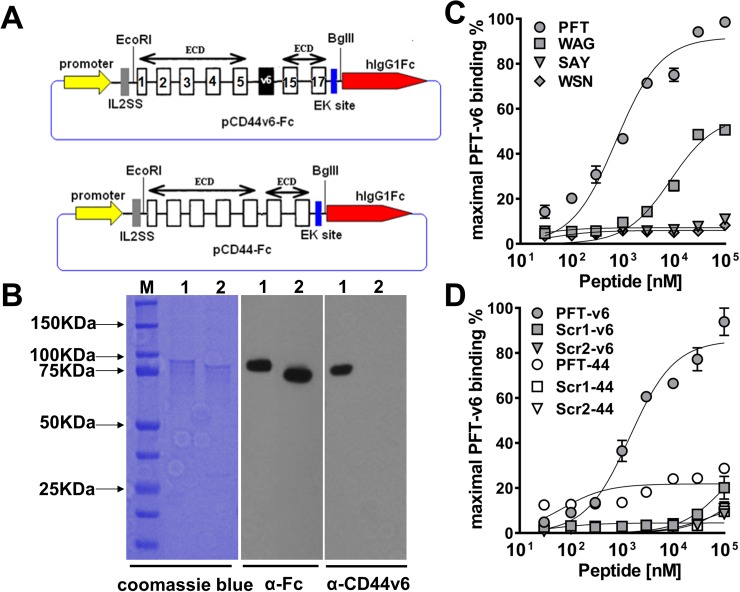
Figure 2. Characterization of peptide binding to recombinant CD44v6.
(A) Schematic of recombinant CD44v6-Fc and CD44-Fc expression construct. The number of constant exons (1-5 and 15-17) are marked. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis and immunoblotting of purified CD44v6-Fc and CD44-Fc (M, BioRad precision plus all blue prestained protein standard; lane 1, CD44v6-Fc; lane 2, CD44-Fc). For SDS-PAGE analysis, the purified proteins were detected by coomassie blue staining. For immunoblotting, the mouse anti-human Fc Ab or mouse anti-human v6 region specific mAb VFF18 was used as the primary Ab and HRP conjugated goat anti-mouse Ab was used as the secondary Ab. (C) ELISA analysis of the dose dependent recombinant CD44v6-Fc binding ability of four biotinylated peptides. The peptides displayed on clone v6p1 (PFT), v6p3 (WAG), v6p8 (SAY) and v6p10 (WSN) were synthesized with a biotin label. The maximal ELISA absorbance value of PFT binding to CD44v6-Fc was used to normalize the binding signal of individual peptides. The specific binding curve was generated using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software and absolute Kd values were calculated using nonlinear regression. (D) The specificity of PFT binding to recombinant CD44v6-Fc. Different concentrations of PFT and its two scrambled peptide versions were incubated with immobilized CD44v6-Fc or CD44-Fc, respectively for ELISA analyses. The maximal ELISA absorbance value of PFT binding to CD44v6-Fc was used to normalize the binding signal of individual peptides. The specific binding curve was generated using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software.