Figure 2.
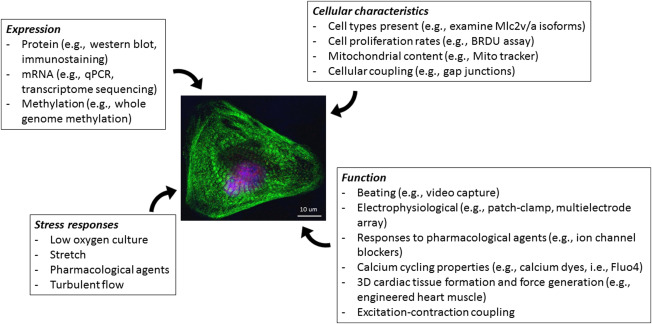
Experimental procedures to consider when performing experiments with PSC‐CMs. Expression: hPSC‐CMs can be analyzed for the expression of proteins, RNA, methylation markings. Cellular characteristics: These methods used to examine the physical characteristics of cells will give insight into many types of diseases, particularly those with functional consequences. Function: The most challenging aspect of using hPSC‐CM is assessing their function. Methods included are specialized and require expert advice. For example, engineered heart muscle is a 3D tissue construct made of mixture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and extracellular matrix which can be formed within ring shaped molds, embedded with rigid posts, or elongated into rigid mesh. These can be used to measure the force of contraction of PSC‐CM, and has also been shown to induce sarcomere assembly and maturation. Patch clamping is the gold standard method for the electrophysiological characterization of cardiomyocytes. Using this method, functionality of the cells, maturity level and even subtype of the cells can be revealed. This method, however is extremely time consuming and low‐throughput. Multielectrode array (MEA) is a non‐invasive method for detection of field potential.This method can be used for high‐throughput safety screening of drugs. Excitation‐contraction coupling can be investigated using dye transfer techniques. Stress responses: Cellular responses to external stress, such as culturing cells in low oxygen level and stretch, can also be used to probe the functionality of hPSC‐CMs characteristics. (see References 41, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 73, 74, 75)
