Figure 5.
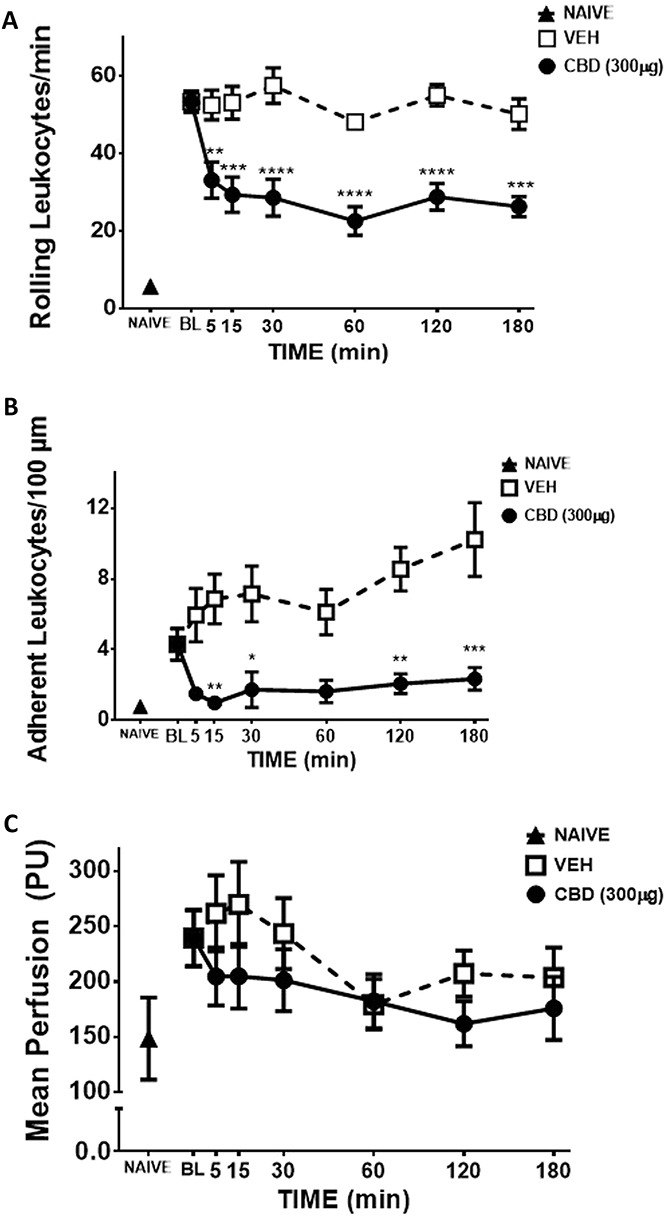
Anti-inflammatory action of CBD on day 1 MIA-induced inflammation. When compared with naïve controls, intra-articular MIA significantly increased rolling (A) and adherent (B) leukocytes, and caused synovial hyperaemia (C) (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, P > 0.05, unpaired t test; n = 6-12). Over a 3-hour time course, CBD (300 μg) significantly decreased leukocyte rolling (A) leukocyte adherence (B) and knee joint blood flow (C) when compared to vehicle. (****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 6). Data are mean values ± SEM. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CBD, cannabidiol; MIA, sodium monoiodoacetate; PU, perfusion unit; VEH, vehicle.
