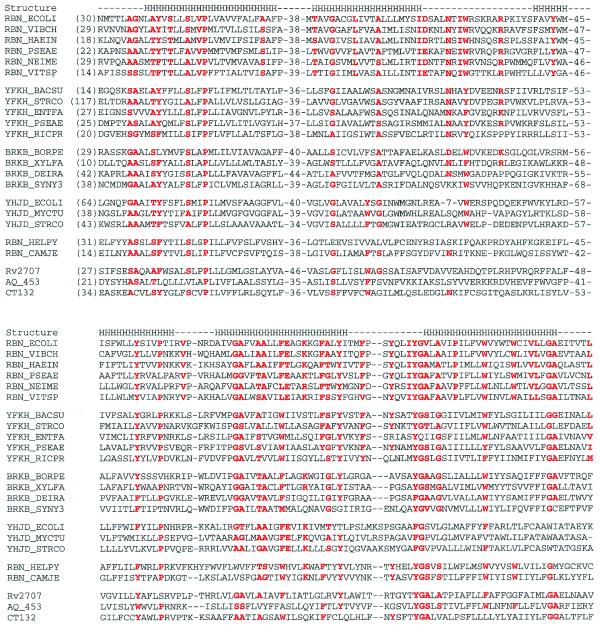
Figure 3.
Sequence comparisons of RBN family proteins. This abbreviated sequence alignment was generated by ClustalX with some editing based on BLAST searches. The sequences are from the NCBI non-redundant protein sequence database. The sequences included are: RBN_ECOLI, E.coli RNase BN (accession no. G418487); RBN_VIBCH, V.cholerae RNase BN (G9657340); RBN_HAEIN, H.influenzae RNase BN (G1176326); RBN_PSEAE, P.aeruginosa RNase BN (G9946857); RBN_NEIME, Neisseria meningitidis RNase BN (G7225749, G7379426); RBN_VITSP, Vitreoscilla sp. RNase BN (G3493604); YFKH_BACSU, B.subtilis transporter homolog yfkH (G7475937); YFKH_STRCO, Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) yfkH homolog (G6425606); YFKH_ENTFA, Enterococcus faecalis yfkH homolog (G3608389); YFKH_PSEAE, P.aeruginosa yfkH homolog (G9948830); YFKH_RICPR, R.prowazekii hypothetical protein RP496 (G7467777); BRKB_BORPE, Bordetella pertussis brkB protein (G2120987); BRKB_XYLFA, X.fastidiosa brkB homolog (G9105274); BRKB_DEIRA, Deinococcus radiodurans brkB homolog (G7473422); BRKB_SYNY3, Synechocystis sp. (strain PCC 6803) brkB homolog (G7469712); YHJD_ECOLI, E.coli yhjD gene product (G586684); YHJD_MYCTU, M.tuberculosis hypothetical protein Rv3335c (G7477578); YHJD_STRCO, S.coelicolor A3(2) putative integral membrane protein (G7649576); RBN_HELPY, H.pylori hypothetical protein HP1407 (G7463952); RBN_CAMJE, Campylobacter jejuni putative RNase BN (G6968645); Rv2707, M.tuberculosis (strain H37Rv) hypothetical protein Rv2707 (G7477329); AQ_453, A.aeolicus hypothetical protein aq_453 (G7517605); CT132, Chlamidia trachomatis hypothetical protein CT132 (G7468636). The secondary structure noted by the letter H for helix is that predicted for E.coli RNase BN by TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-1.0/). All other superfamily members are predicted to have a similar secondary structure. Secondary structure predicted by PredictProtein (http://cubic.bioc.columbia.edu/predictprotein/) gave similar results, but with more helices at the N-terminus and the putative loop regions. Residues that are highly conserved in RNase BN and its homologs are highlighted in red. Corresponding residues in other subfamilies are also highlighted if they are conserved.