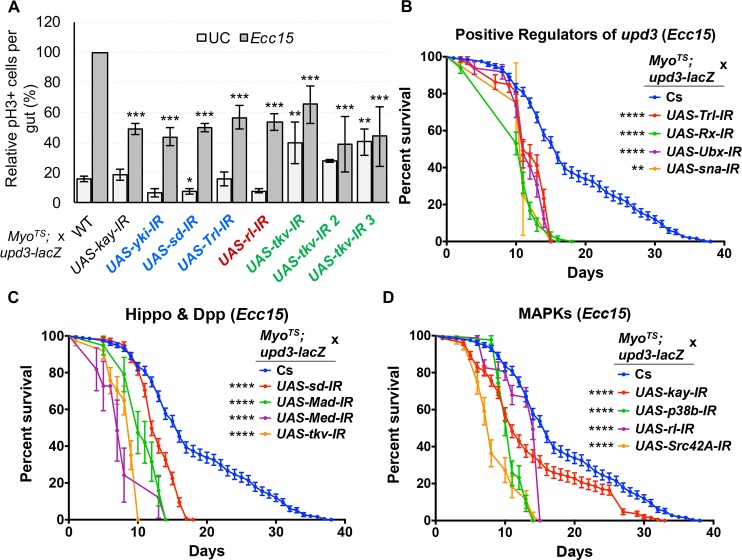
Fig 7. ISC proliferation and survival following Ecc15 infection are compromised by inhibition of the TFs and pathways that are required for upd3 induction.
(A) Total pH3+ cell counts in unchallenged and Ecc15 infected guts demonstrate that knockdown in ECs of D-Fos, yki, sd, Trl, and sna as well as upstream components of the MAPK and Dpp pathways is accompanied by a decrease in ISC mitotic activity. Statistical significance: mean values of at least 3 repeats are represented ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (student’s t test). (B-D) Survival curves of flies orally infected with Ecc15 alongside RNAi-induced knockdown of indirect upd3 regulators (B), Hippo and Dpp pathways components (C), or MAPK pathway factors (D). Curves represent averaged survival ± SE. Statistical significance: *p<0.0332, **p<0.0021, ***p<0.0002, ****p<0.0001 (Log-rank test).