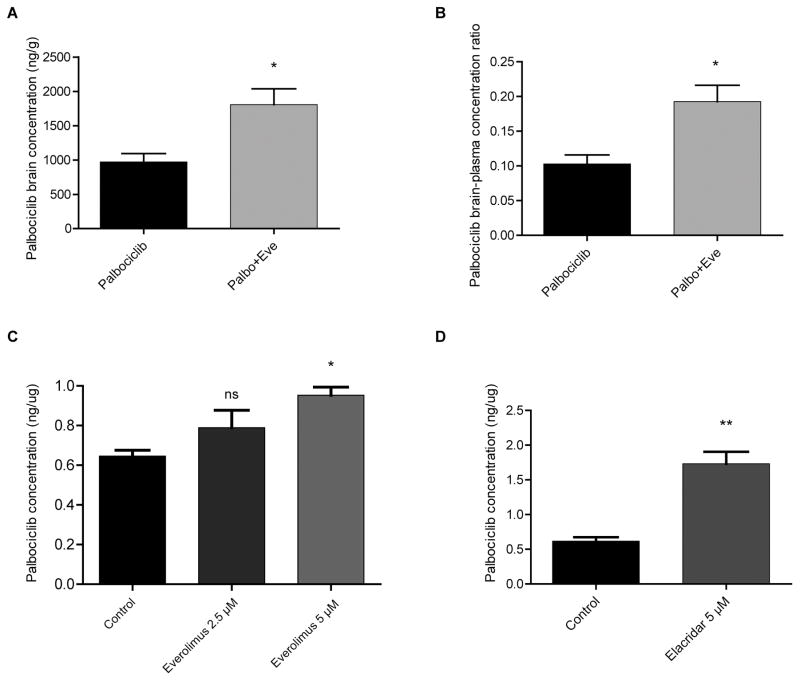
Figure 4. Everolimus significantly increases brain concentration of palbociclib.
(A) Brain concentration and (B) brain-to-plasma concentration ratio of palbociclib either alone or in the presence of everolimus following three days of once-daily oral treatment in wild type mice (n =4; values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; two-tailed t-test). (C–D) Everolimus co-administration drives a moderate increase in intracellular palbociclib concentration in human brain microvascular endothelial cells, as does the very potent P-gp and BCRP inhibitor elacridar (*P = 0.01; **P < 0.003; two-tailed t-test).