Fig. 3.
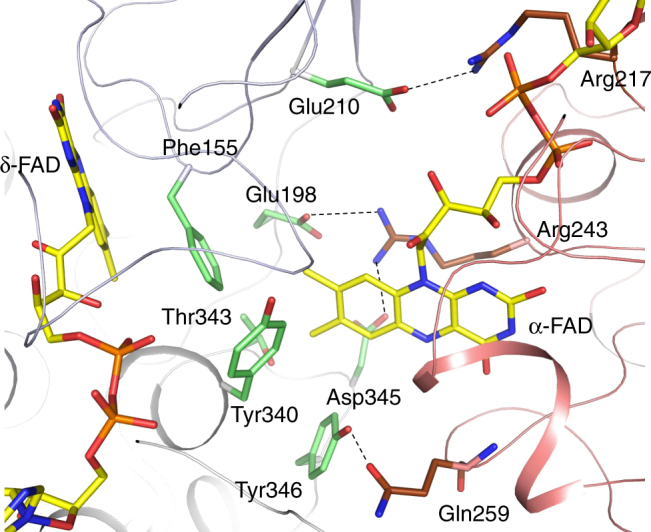
Coupling site between α-FAD and δ-FAD in the D state. The isoalloxazine rings are oriented perpendicularly to each other with the xylene ring of α-FAD pointing towards the Si-side of the isoalloxazine ring of the δ-FAD. The binding sites for β-FAD and δ-FAD are virtually identical in D and B-like states; substantial differences exists for α-FAD. The exposed xylene ring of α-FAD is flanked by predominantly hydrophobic side chains (carbon in green) from the Bcd dimer (white blue, grey). Phe155 of Bcd1 is in van der Waals contact to both isoalloxazine rings. The shortest distance between α-FAD and δ-FAD is between the C8 methyl groups. The ADP and ribitol moieties of α-FAD are surface-exposed and only contacted to Bcd via a layer of solvent molecules. The rather weak interaction between Bcd and α-FAD supports a quick detachment process required for catalysis
