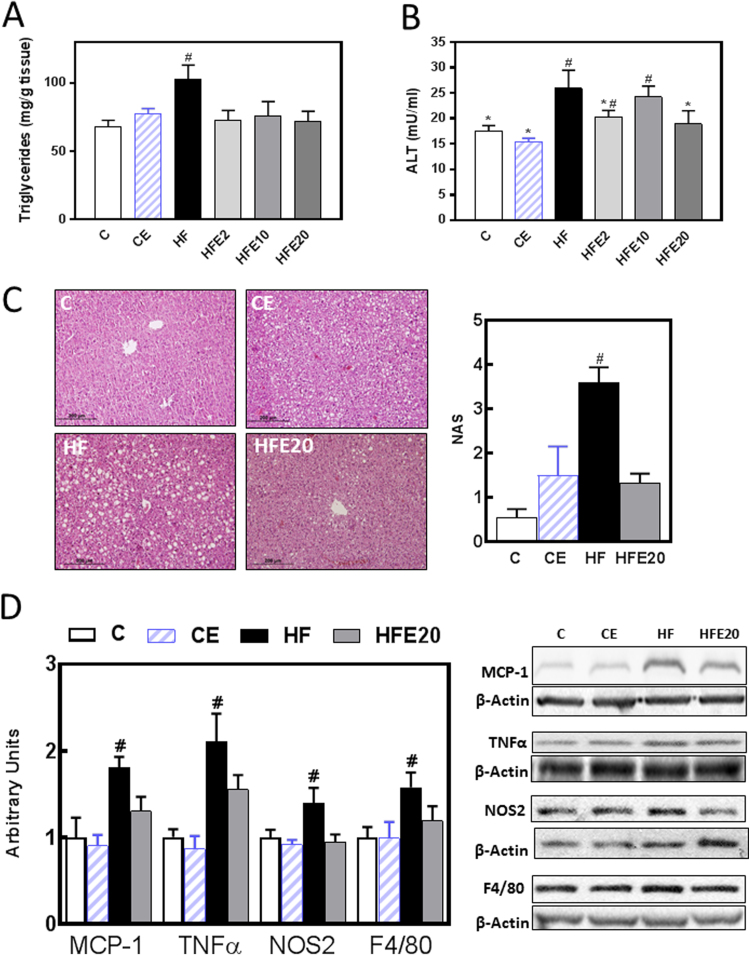
Fig. 2.
Effects of EC supplementation on steatosis and hepatic inflammation. Mice were fed a control diet (empty bars), the control diet supplemented with 20 mg EC/kg body weight (dashed bars), a HFD (HF) (black bars), or the HFD supplemented with 2 (HFE2), 10 (HFE10), or 20 (HFE20) mg EC/kg body weight (grey bars). On week 15 on the corresponding diets the following parameters were measured: A-liver triglyceride content, B- plasma alanine amino transferase (ALT) activity, C- fat liver deposition and NAFLD activity score (NAS) evaluated by hematoxylin/eosin tissue staining, D-proteins involved in inflammation: MCP-1, TNFα, NOS2 and F4/80 protein levels were measured by Western blot. Bands were quantified and values referred to β-actin levels (loading control). Results for HF, HFE20 and CE were referred to control group values (C). Results are shown as mean ± SE of 5–8 animals/group. A,B- Values having different symbols are significantly different; C,D- #Significantly different from all other groups; (p < 0.05, one way ANOVA test).