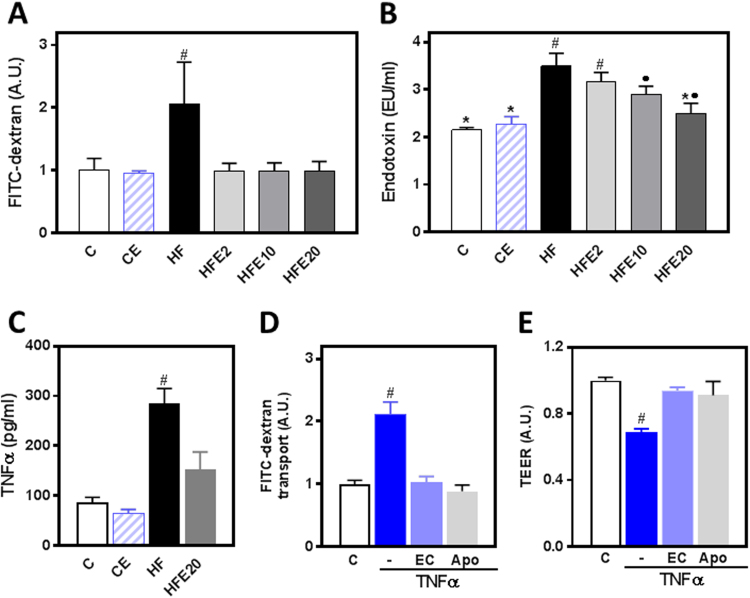
Fig. 3.
Effects of EC on epithelial barrier permeabilization induced by HFD consumption in mice and by TNFα in Caco-2 cells. A,C- Mice were fed a control diet (empty bars), the control diet supplemented with 20 mg EC/kg body weight (dashed bars), a HFD (HF) (black bars), or the HFD supplemented with 2 (HFE2), 10 (HFE10), or 20 (HFE20) mg EC/kg body weight (grey bars). Intestinal permeability was evaluated by measuring at week 13 FITC-dextran permeability (A), and at week 15 plasma endotoxin (B) and TNFα (C) concentrations. Results are shown as mean ± SE of 5–8 animals/group. D- FITC-dextran transport and D- TEER in Caco-2 cells. Polarized cells were incubated for 6 h at 37 °C in the absence of additions (control, C); or after addition of 5 ng/ml TNFα to the lower chamber in the absence (TNF) or the presence of 1 μM EC or 1 μM apocynin (Apo) added to the upper chamber. Results are shown as mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. A,C-E- #Significantly different from all other groups; B-Values having different symbols are significantly different; (p<0.05,one way ANOVA test).