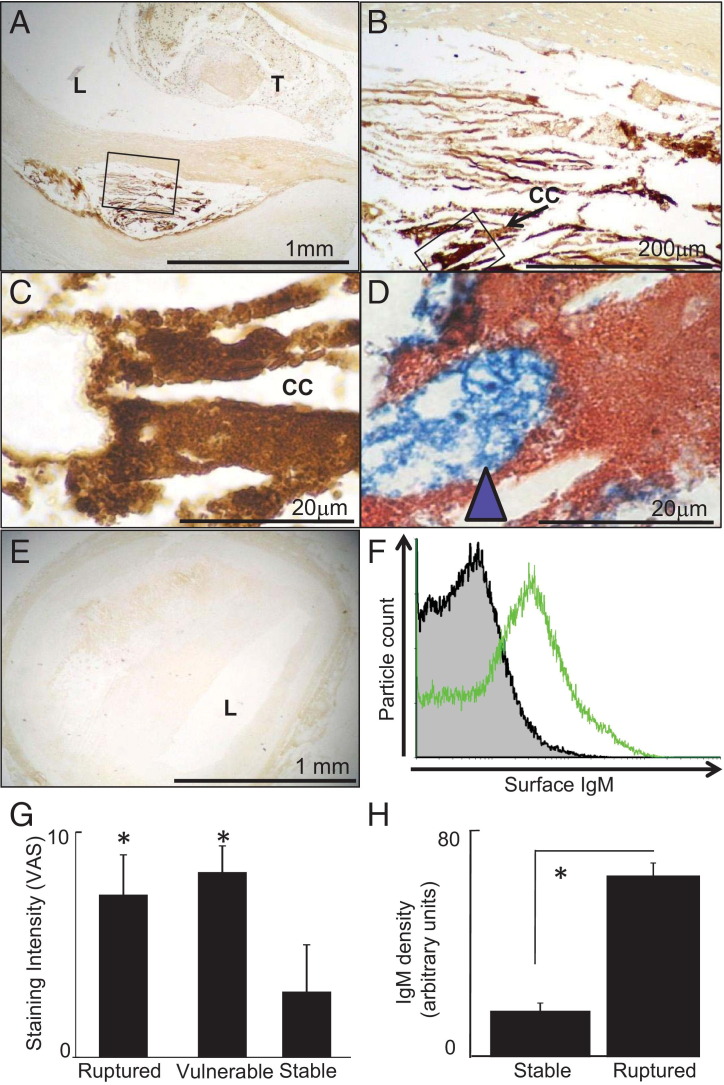
Figure 8.
Ruptured plaques and vulnerable lesions contain IgM in contact with macrophages. Immunostaining for IgM was conducted on coronary atherosclerotic lesions responsible for coronary thrombosis and cardiac death (ruptured plaques) in comparison with unruptured coronary lesions from the same patients (vulnerable lesions) and coronary lesions from patients who had died of noncardiac causes (stable lesions). Scale bars indicate distances. Ruptured lesions have increased IgM deposits coating lipid core debris. A-C: Photomicrographs at successive magnifications of a representative culprit plaque immunostained for IgM; brown, positive immunopositivity; blue, nuclei; T, thrombus; L, lumen; CC, example cholesterol cleft. B: High power of box in A. C: High power of box in B; IgM covers granular lipid core debris structures. D: Representative micrograph of lipid core of ruptured plaques double-immunostained for IgM (red) and CD68 (blue). IgM-positive lipid core debris (red) is in intimate contact with macrophages (blue arrowhead). E: Representative micrograph of (unruptured) plaque from an autopsy with death due to a noncardiac cause, immunostained for IgM along with the ruptured plaque shown in A. F: Flow cytometry of plaque debris recovered from an advanced (calcified and slightly ulcerated) aortic plaque, representative of n = 3. The x axis shows surface IgM staining and the y axis particle number. Shaded gray histogram, isotype control. Open green histogram, anti-IgM–FITC. G: Ruptured plaques and vulnerable lesions have consistently more IgM than stable lesions. We examined culprit lesions from fatal MI cases, vulnerable lesions from the same case, and stable plaques from cases with a clear positive noncoronary cause of death. Each plaque had IgM immunostaining intensity scored on a 0- to 10-point continuous visual analog scale. This is a conceptual extension of the common 0, 1, 2, 3 scale to validly allow parametric data methods. Gaussian distribution was checked with a stem-and-leaf plot. The mean and SE were determined for each group of patients (n = 10 MI cases, n = 16 non-MI controls); *P < 10−5, significant difference, analysis of variance. H: We then performed a focused corroborative reanalysis of IgM in ruptured lesions in MI cases and stable lesions in non-MI controls using computer-aided morphometry as previously described.24 The area of brown pixels and the pixel intensity brownness were integrated to express a semiquantitative measure of IgM density, along the lines of Western blot quantification. The IgM was quantified for each patient and expressed as mean ± SE for each group of patients. Ruptured plaques have increased IgM (*P < 10−5, Student's t-test) using this method.