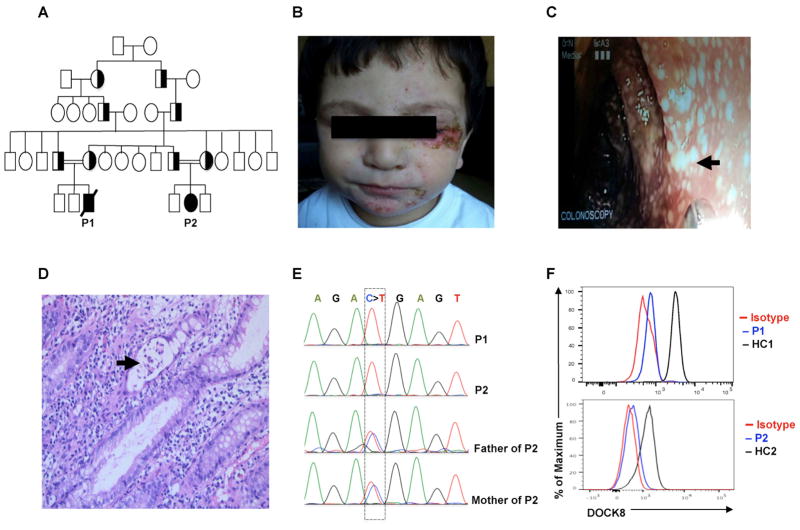
Fig. 1. Identification of autosomal recessive DOCK8 mutation in two patients with IPEX-Like phenotype.
(A) Pedigree of the extended family of patients P1 and P2. Squares represent males while circles for females. Filled symbol denote patients, and half-filled symbols denote carriers. The double lines between the parents indicate consanguinity. (B) Representative picture showing facial eczematous lesions in P1 with secondary bacterial infection. (C) Large intestinal mucosal lesions in P1 identified by colonoscopy. (D) Tissue pathology of active colonic lesions in P1. Arrow indicates a crypt abscess. (E) Sanger sequencing fluorograms showing germline homozygous DOCK8 mutation in patients P1 and P2 and its heterozygous carriage in the parents of P2. (F) Flow cytometric analysis of DOCK8 expression in CD3+ T cells of P1 and P2 as compared to those of healthy controls.