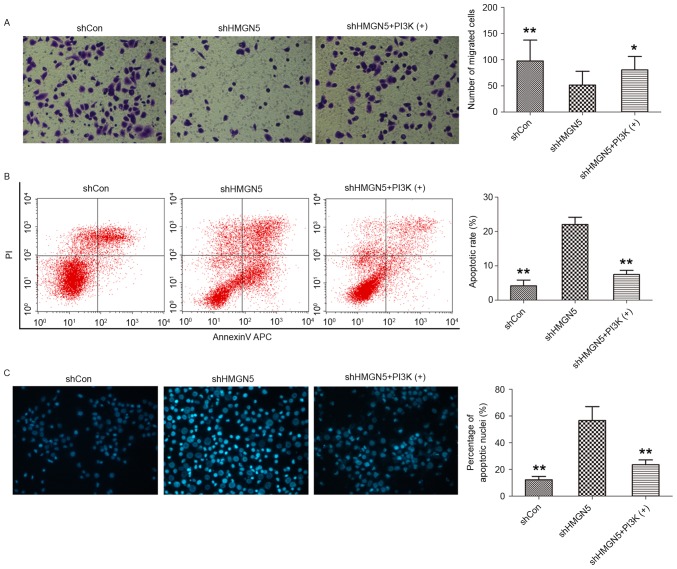
Figure 4.
HMGN5-knockdown inhibits invasion but increases apoptosis in UBC cells. (A) Following infection with lentivirus, 5637 cells were treated with CDDP, with or without IGF-1 (left panels). The Transwell assay was then used to detect cell invasion. The cells penetrating the Matrigel were stained with crystal violet and shown as blue under a light microscope (magnification, ×200). Quantitative analysis of the number of migrated cells in different groups (right panel). (B) After infection, the cells were treated with indicated agents for 24 h, followed by staining with Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate and PI and analyzed by flow cytometry (left panels). Quantitative analysis of the rate of early apoptosis in different groups (right panel). (C) Hoechst 33342 staining was employed to observe the morphological change of apoptotic cells (left panels; magnification, ×200). Cell nuclei with apoptosis were characterized by pyknosis, shrink and karyorrhexis and exhibited the marked fluorescence under fluorescence microscope. Quantitative analysis of the percentage of apoptotic nuclei in different groups (right panel). Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with HMGN5 knocked down 5637 cells. HMGN5, high mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; sh, short hairpin; Con, control; PI, propidium iodide.