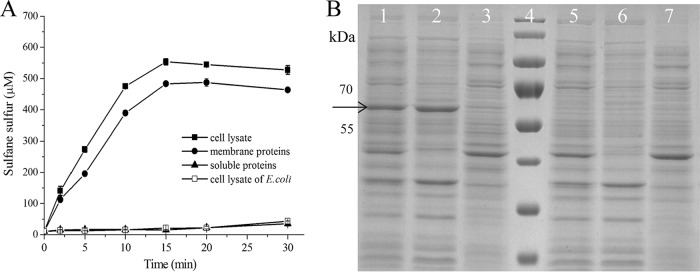
FIG 2.
Detection of CpSQR in cellular fractions. E. coli(pET-Cpsqr) was used to isolate the cellular components. The whole-cell lysate (832 μg of protein ml−1), the membrane component (266 μg ml−1), and the soluble proteins (470 μg ml−1) in Tris buffer (pH 8) were obtained. The whole-cell lysate (665 μg of protein ml−1) of E. coli BL21 was used as the negative control. (A) CpSQR activities were shown as sulfane sulfur production. All the fractions were diluted 1:5, and Na2S was added to 1,000 μM to initiate the reaction. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis with cellular components. Lanes 1 to 3, E. coli (pET30-Cpsqr). Lane 1, whole-cell lysate; lane 2, membrane component; lane 3, soluble proteins. Lane 4, marker. Lanes 5 to 7, E. coli control. Lane 5, whole-cell lysate; lane 6, membrane component; lane 7, soluble proteins. Ten micrograms of proteins of each sample was loaded. The arrow points to the position of CpSQR.