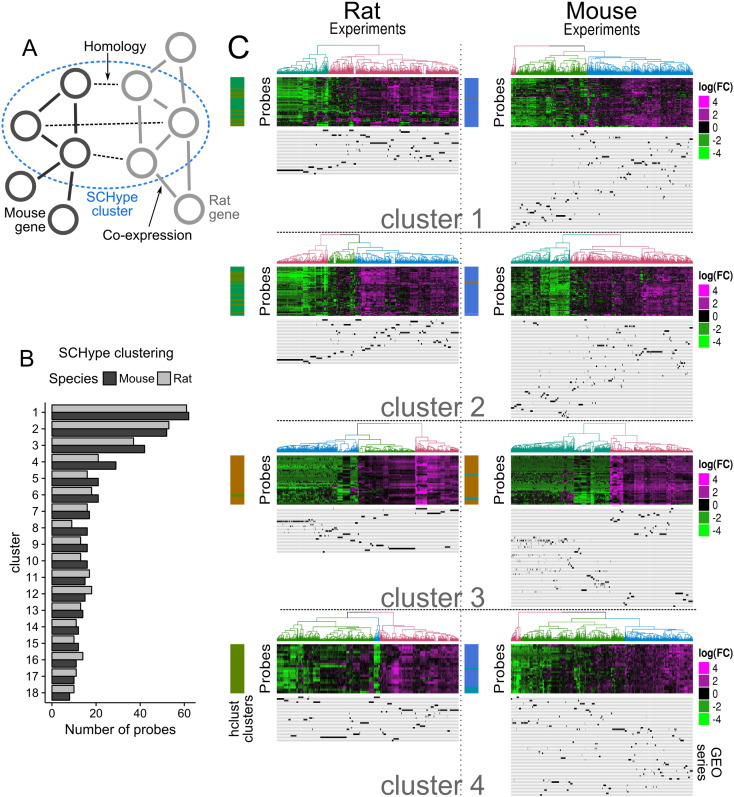
Fig. 3.
Co-clustering of rat (middle) and mouse (right) liver data using SCHype. A. SCHype is a clustering tool for hypergraphs, built here from two co-expression graphs and an homology graph. B. Number of mouse (dark grey) and rat (light grey) probes for the SCHype clusters with more than 10 probes for each species. X-axis: number of probes included in each SCHype cluster. Y-axis: SCHype predicted clusters, numbered according to the number of probes per cluster in decreasing order. C. The biggest four SCHype clusters are shown. Genes in mouse and rat in each cluster are homologous to each other. The results of hierarchical clustering for each species is shown as a colour bar on the left. Colour-code matches the experiments trees in Fig. 1. Under the heatmap, clustering localisation of experiments from each series is shown in black, one line per series. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)