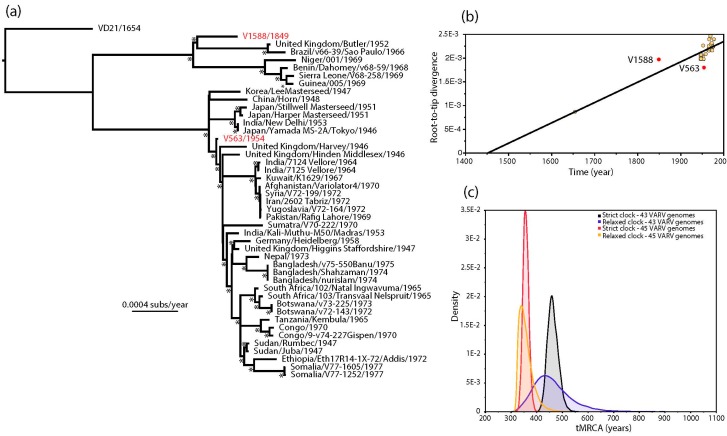
Figure 1.
(a) Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of 45 complete genomes of VARV. The phylogeny was based on a complete genome alignment of 181,261 bp constructed using a combination of MAFFT [11] and GBlocks [12] pruning to remove ambiguously aligned regions. The phylogeny was inferred using PhyML [13] assuming the General Time Reversible (GTR) model of nucleotide substitution, with a proportion of invariable sites (I) and a gamma distribution (Г) of among-site rate variation. All horizontal branch lengths are scaled according to the number of nucleotide substitutions per site, and bootstrap values >90% are marked with a * symbol. The tree is rooted using a sequence obtained from a Lithuanian mummy (VD21) and V1588 and V563 are shown in red; (b) regression of root-to-tip genetic distances from the ML tree against their sampling year. V1588 and V563 are shown in red. This analysis was performed using the TempEst program [14]; (c) bayesian estimates of times to common ancestry in VARV. The ’45 VARV’ estimates utilized the tip times in the full 45 genome sequence data set, incorporating mean age estimates of 1849 and 1954 for V1588 and V563, respectively, that are taken from the distribution of possible racemization-based dates provided by Pajer et al. [1]. The ’43 VARV’ estimates are those in which a uniform prior distribution with bounds of 0 and 1.0E10 was specified for the ages of V1588 and V563, with these and all other parameter values inferred from the remaining 43 sequences in the alignment. All these analyses were performed using the BEAST package [8], run for 100 million generations, and employing a constant population size (XML files are available in the supplementary material).