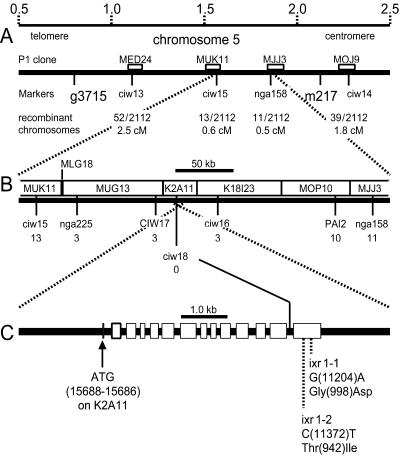
Figure 1.
Map-based cloning of the IXR1 gene. (A) Representation of a region of Arabidopsis chromosome 5 showing a megabase-scale (Upper), the position of RFLP markers g3715 and m217, SSLP markers CIW13, 14, 15, and SSLP marker nga158. Chromosome 5 P1 clones (http://www.kazusa.or.jp/arabi/) containing the SSLP markers are represented by white boxes. The number of recombinant chromosomes (meiotic breakpoints) in a total of 2,112 examined chromosomes, found for each marker and their calculated genetic distance to the IXR1 locus [in centimorgans (cM)], is given. (B) The region containing the flanking SSLP-markers CIW15 and nga158, showing the position and the number of recombinants found for CAPS (CIW17, PAI2) and SSLP (CIW16, 18) markers and the nonoverlapping parts of P1 and TAC clones spanning the region. (C) An 8-kb segment of TAC clone K2A11 (nucleotides 17, 500–9, 500) showing the intron/exon structure of the IXR1 gene (note crossover of the dotted lines). The start codon and the point mutations in the ixr1–1 and ixr1–2 alleles in the last exon and the predicted amino acid exchanges in the mutant gene products are indicated.