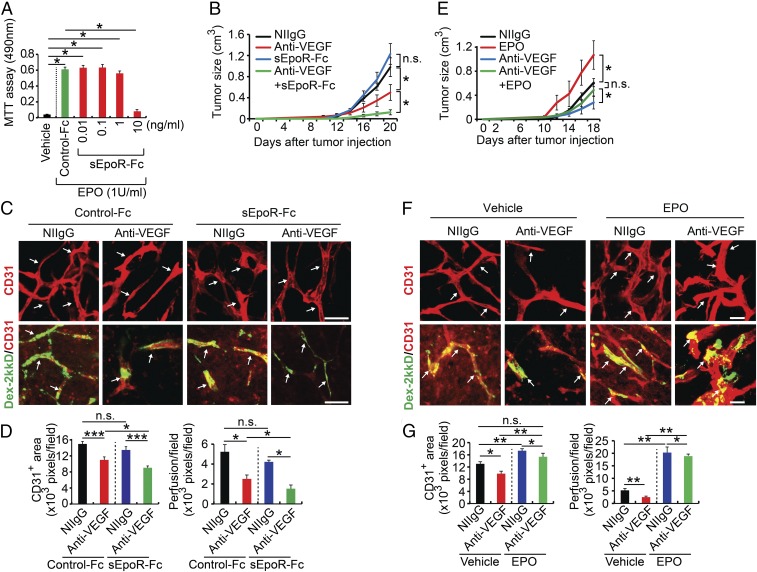
Fig. 3.
Kidney-derived EPO confers anti-VEGF resistance. (A) Proliferation assay of sEpoR-Fc and control Fc-treated UT-7/EPO in the presence or absence of EPO protein (n = 6 samples per group). (B) Tumor growth rates (n = 6 animals per group). (C and D) Immunohistochemical analyses of CD31+ microvessels and vascular perfusion of 2,000-kDa dextran. Arrows in C, Upper point to CD31+ blood vessels and in Lower indicate perfused dextran+ signals. Quantifications of CD31+ vessel density and dextran blood perfusion (n = 10 samples per group). (E) Growth rates of various monotherapy- or combination therapy-treated LLC tumors (n = 6 animals per group). (F and G) Immunohistochemical analyses of CD31+ microvessels and vascular perfusion of 2,000-kDa dextran. Arrows in F, Upper point to CD31+ blood vessels and in Lower indicate perfused dextran+ signals (n = 10 samples for each group). Quantifications of CD31+ vessel density and dextran blood perfusion (n = 10 samples per group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant. Data are means ± SEM. (Scale bars: 50 μm.)