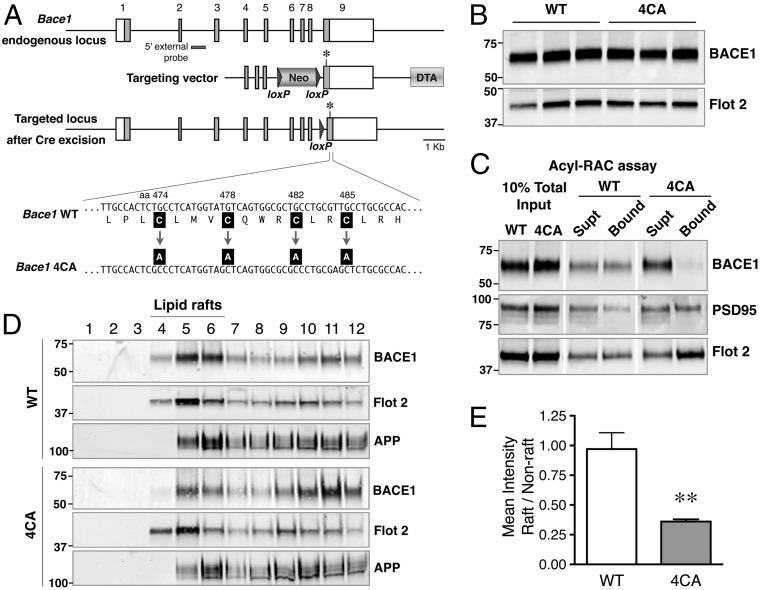
Fig. 1.
Generation of 4CA knock-in mice. (A, Top) Schematic representation of the Bace1 locus showing the nine exons (numbered); coding regions are shown as filled gray boxes. (Middle) The homology arms of the targeting vector are shown along with the loxP-flanked PGK-Neo and the Diptheria Toxin A (DTA) selection cassettes. An asterisk indicates a silent mutation introduced to generate a unique SacI site in the mutant allele. (Bottom) Schematic structure of the targeted allele after Cre-mediated excision of the PGK-Neo gene. The cysteine-to-alanine substitutions are indicated. (B) Total brain homogenates of WT and 4CA mice (P7) were analyzed by immunoblotting. (C) Detection of S-palmitoylated BACE1 in mouse brain by acyl-RAC. Mouse brain lysates (P7) were subjected to acyl-RAC, and aliquots of captured proteins (Bound) and unbound fraction (Supt) were analyzed by immunoblotting for BACE1, PSD95, and Flotillin 2. (D) P7 mouse brain was homogenized in a buffer containing 0.5% Lubrol WX at 4 °C for 30 min. The lysates were then subject to flotation sucrose density gradient, and an equal volume of each fraction, harvested from the top, was analyzed by immunoblotting. Fractions 4 to 6 represent the interface between 5% and 35% sucrose in the gradient and are enriched in lipid raft marker Flotillin-2. (E) Quantification of the relative distribution of BACE1 in lipid raft and nonraft fractions. **P < 0.01.