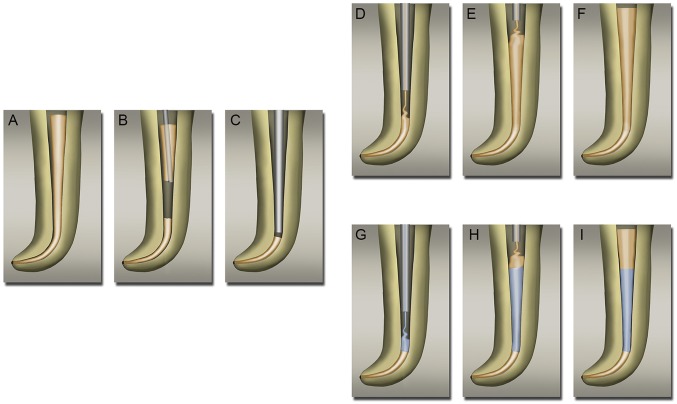
Fig. 3.
Control and NDGP obturation process. (A) Master GP cone placed with zinc-eugenol sealer. (B) Removal of excess GP with heated plugger. (C) Condensing master GP to apical 5 mm. (D) Canal space filled with GP, using extruder starting from apical end. (E) Canal space filled with unmodified GP up to cervical third. (F) Fully condensed and completed obturation with unmodified GP. (G) Middle third of the canal space was filled with NDGP, using extruder that started from the apical end. (H) Cervical third of the canal space was filled with unmodified GP. (I) Fully condensed and completed obturation with NDGP in the middle third of the canal.