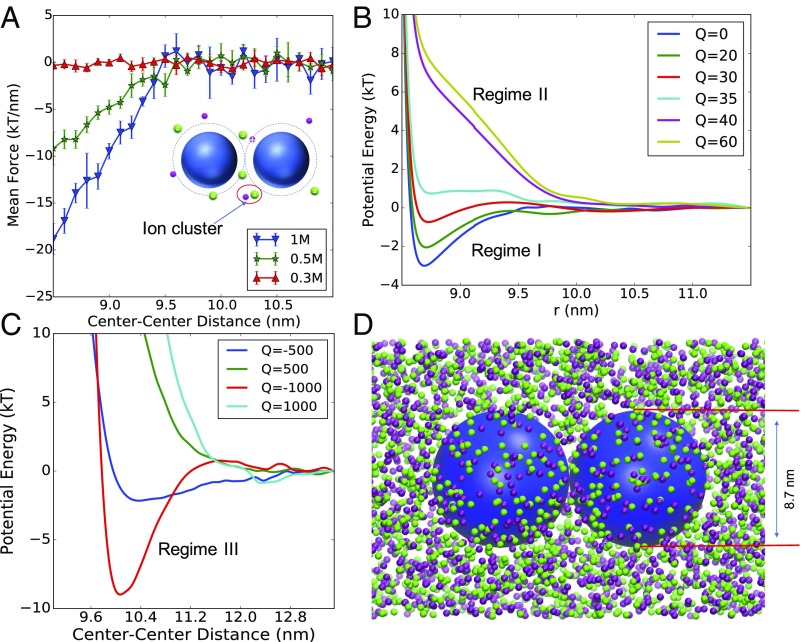
Fig. 2.
Interactions between NPs in NaCl solutions. (A) Simulated average force between two electroneutral NPs in solutions with different NaCl concentrations. (B and C) NP–NP Interaction potentials in 0.5 M NaCl, calculated from integration of simulated force for NPs with different charges. NPs have an effective diameter of 8.7 nm. The charge Q is in elementary charges (for example, Q = 20 corresponds to a surface charge density of 0.084 e/nm2). As the NP surface charge density increases in B, the interaction changes from regime I to regime II as discussed in Fig. 1. In C, the potential is strongly repulsive at small surface–surface distance, and has a potential well for negatively charged NPs, the corresponding NP charge density is referred to as regime III. (D) Snapshot of MD simulation probing the interaction between two NPs immersed in 0.5 M NaCl salt. Small purple and green beads represent sodium and chloride ions, respectively. Large blue spheres represent the NPs. Sizes of the ions are not to scale.